“Cancer is a chapter in your life, not your whole story.”
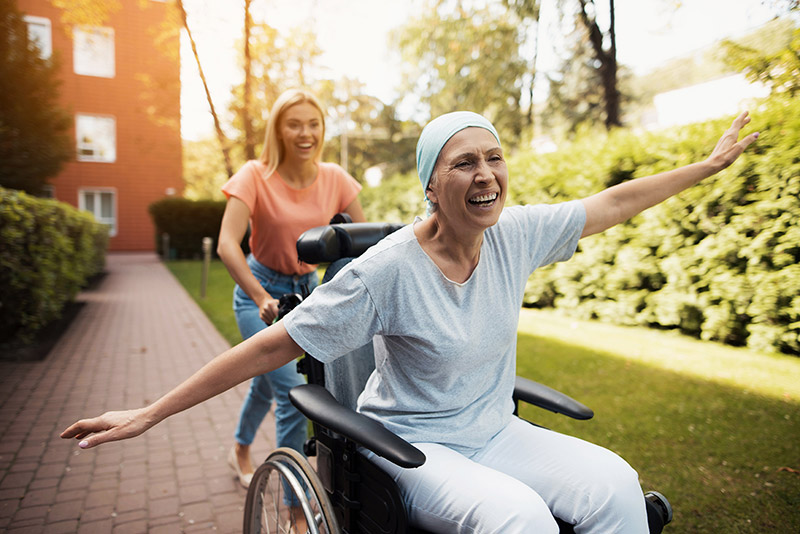
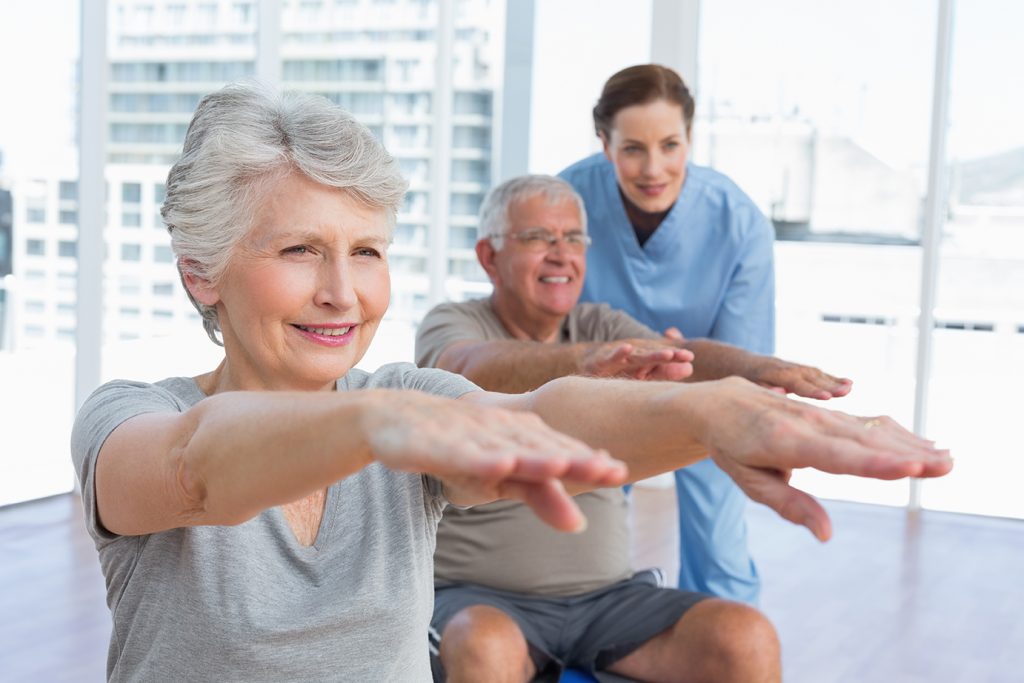
To the ones who have fought cancer or witnessed someone fighting cancer, very well know that the after-life is challenging. It’s better to be prepared for the ‘newness’ that will arrive unannounced than become anxious about it. There are certain do’s and don’ts that one can follow to make the beautiful life, you fought for, more beautiful. After a heroic journey of battling cancer, one would face several challenges to cope up with the new normal life. It can right from dealing with long-term or short-term illnesses that can be caused due to cancer, coping with the mental health and physical health post the surgery, or even the simplest task of meeting your peers and colleagues again. Your everyday life just takes a drastic turn. Let’s take a pause here and learn how to manage these challenges for a better living. After all, you fought only so that you could get back on track!
Here are certain Do’s that you can follow after a Cancer Surgery
GIVE TIME
Time heals. In this case, be it cancer or coping with the after-life. Just as you are dealing with yourself and taking the time to accept the new changes, the people around you are doing the same. Give each other the time to learn and adjust what might work or not work going forward. Your new lifestyle will not only bring changes in your life but also in the life of people around you. So, give time and take time to understand the same.
FOLLOW-UP & MEDICATION
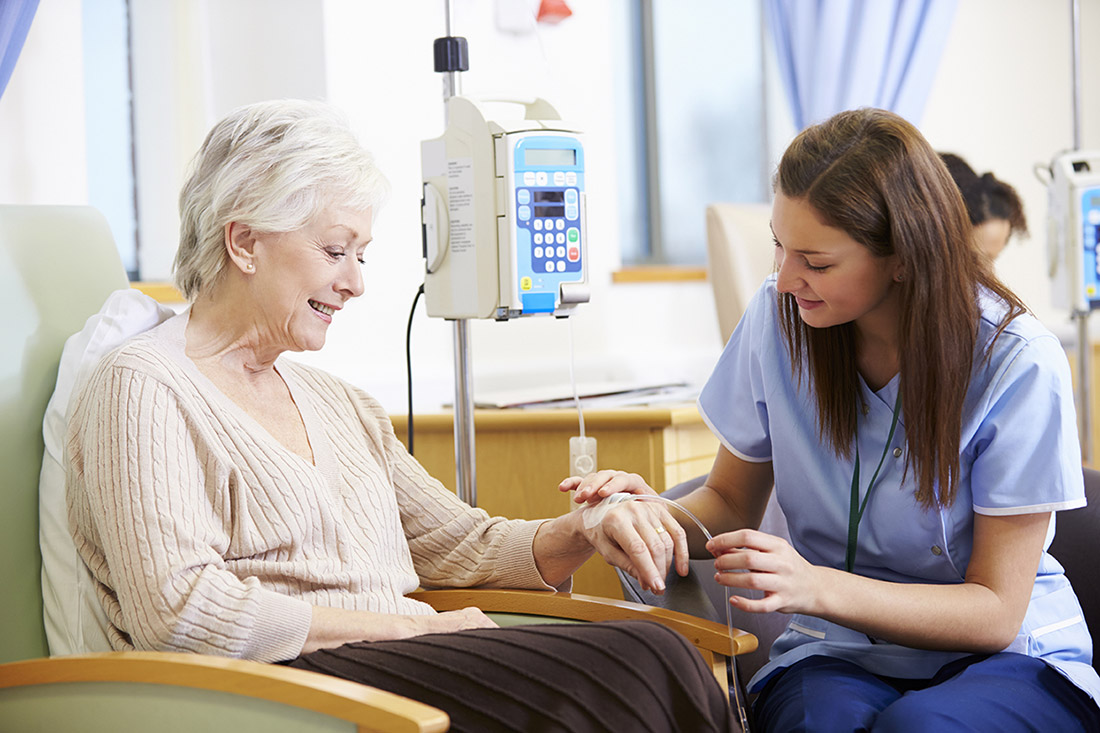
While you have successfully defeated cancer, it is equally important to keep visiting the doctor as and when requested after the surgery. There’s a lot that your doctor needs to examine even after months of the surgery and hence it is paramount to not miss follow-ups along with the prescribed medication by your doctor. These factors are directly linked to your recovery rate and survival.
STAY POSITIVE
It’s easy to go on a negative trail of thoughts about cancer and your life. But keep in mind that it will only affect you and your mental being. Divert your energy in positive thinking. Indulge in tasks that made you happy or find new interesting ones. Meditation, yoga, new hobbies will help resurrect your mental health, which is paramount.



TALK IT OUT
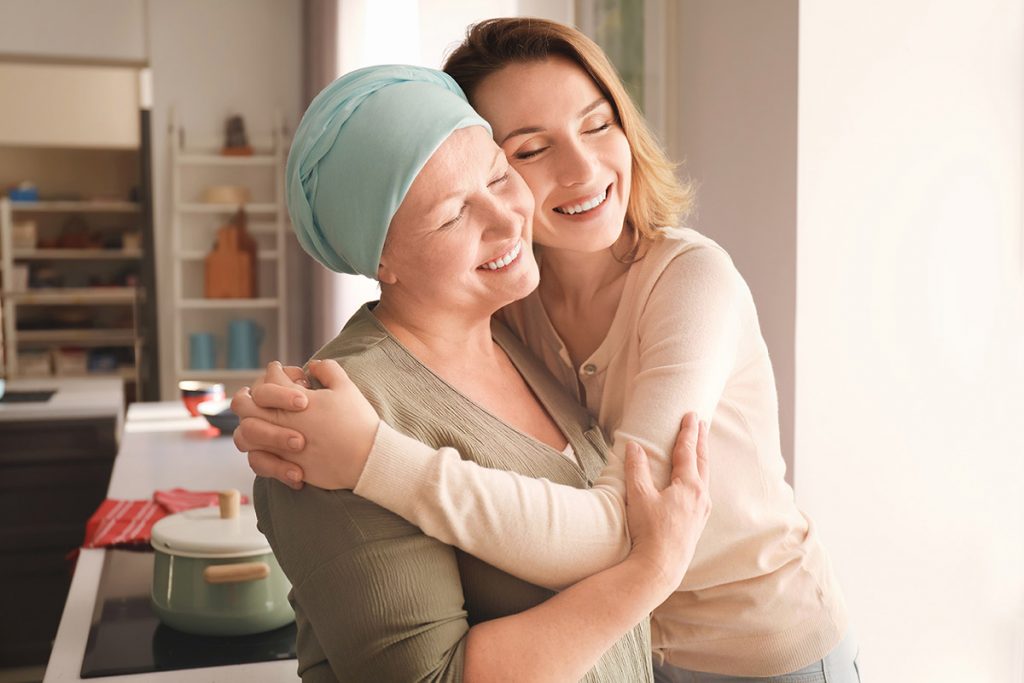
Talking not only helps you, but also the people around you; to know how you are feeling. You could talk to anyone – your parents, peers, colleagues, partners, or even medical experts. Your fears, doubts, expectations, feelings all fall in place once you put them into words. Journaling too is a great way of dealing with internal conflicts. Know that people around you are all ears. All you have to do is talk it out.
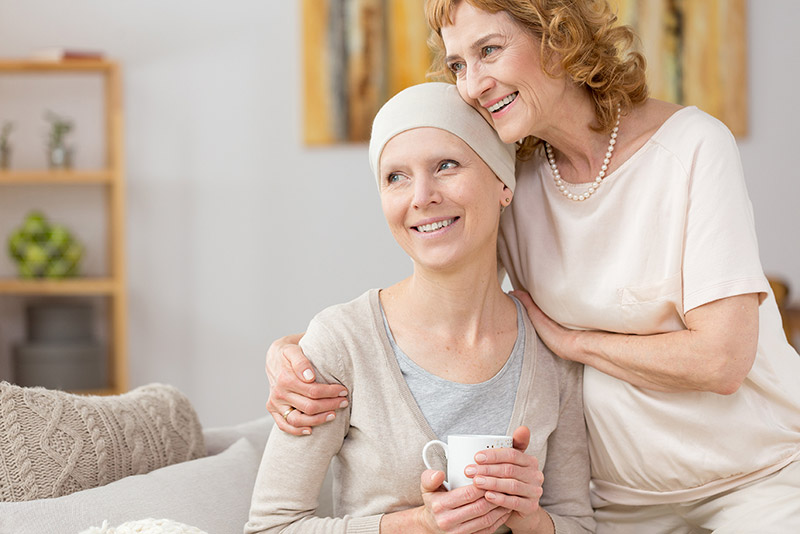



While there are certain dos, there are also a few don’ts to keep in mind.
DON’T SLACK
The last thing you want to do is be in that bed forever. Do not let the slacking feeling take over you. Get out and get active. It only gets easier once you take the first step. Start reading, listen to music, kickstart the project you wanted, exercise, meet people. Just. Don’t. Slack. You did not fight to stay in bed, you fought to LIVE. So, let’s get going!
DON’T CONTROL
Keep in mind that the recurrence of illness is not in your hands. Don’t try to control the feelings, people, things, and your health. Just go with the flow and live every moment that you fought for! Controlling is not the solution. But accepting and dealing with is. Make sure you follow the medical procedure and surround yourself will all the affection that you deserve!



After all, the flower that blooms in adversity, is the most beautiful of them all. Keep in mind that you are a cancer survivor and remember that you are one of those million survivors who fought their way back to life and will continue to lead a fulfilling life.