Introduction
Often, many people ignore those symptoms of mild heartburn or minor yet unusual discomfort of chest or shoulder pain, considering it an age-related normality. Sometimes, some might not even feel any symptoms of nerve damage, called neuropathy. This condition is commonly the result of poorly managed and controlled diabetes. Diabetes is a silent threat to the overall health of the patient since it often comes with no warning signs, taking people by surprise with its damage and severe consequences.
According to a study by the Indian Council of Medical Research, nearly 10.1 crores people have diabetes, and approximately 15.3 % of the population of India is pre-diabetic. These disturbing statistics indicate the dire need for awareness about the disease among the masses, effective prevention measures and strategies by agencies like the World Health Organization, and immediate treatment interventions by medical professionals to curb the onslaught of this silent killer.
Diabetes elevates cardiovascular diseases, and diabetic patients have higher risks of heart attack, stroke, nerve damage, and kidney failure, to name a few. To find out how, continue reading this blog.
About Diabetes, its Causes and Types
As a chronic health condition that is not only common in older people but prevalent in children and young adults also, diabetes is emerging as a health crisis, requiring strict and aggressive control and management. A disease that does not affect only one or two body parts but gradually and slowly affects one’s overall health if poorly managed and controlled. What starts as a sugar buildup damages various body parts like heart, kidney, eyes, nerves and blood vessels.
Diabetes is a condition when the sugar levels in the blood increase beyond the medically acceptable threshold limits. The pancreas releases a hormone, insulin, that enables the cells to convert food into energy by absorbing the sugar produced by the food. Often, when the pancreas stops producing or produces insufficient insulin, or the cells cannot utilize the insulin properly, the sugar levels in the bloodstream rise, leading to diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes could be genetic or acquired. The causes of diabetes depend on the type of diabetes. The various types of diabetes and their causes are –
- Type 1 Diabetes (type 1D)– Type 1D is an autoimmune disease where the immune system, by mistake, attacks and destroys the body’s own cells that make insulin. It is also known as insulin-dependent disease. The body cannot produce insulin, and the glucose is unabsorbed, resulting in its buildup in the bloodstream. This type of diabetes is caused genetically and is more common in children and young adults. Daily Insulin injections become a must for a patient’s survival.
- Type 2 Diabetes (type 2D)- Type 2D is an acquired disease caused by obesity, lifestyle, and other environmental factors. It is an insulin-resistant disease where the cells do not properly use the insulin the body produces. The disease is manageable through medications and a healthy lifestyle, including a controlled diet, exercise, and other alternate treatment modalities.
- Prediabetes- A condition where the sugar levels are above the normal limits but not as high as to be considered as type 2D. However, pre-diabetic patients are susceptible and liable to develop diabetes sooner or later if not managed and controlled timely.
- Maturity Onset Diabetes in Young Adults (MODY) – Mutation in a single gene, if inherited by the child, may cause the chances of him/her developing MODY. This disease can be caused irrespective of the person’s weight or lifestyle. Timely and proper diagnosis helps control and manage it effectively.
- Gestational Diabetes- Pregnant women may experience a rise in sugar levels that may attain normalcy after pregnancy. Weight gain and hormonal changes are considered responsible for gestational diabetes.
How Does Diabetes Elevate CVDs?
As an independent risk factor for CVDs, diabetes contributes massively to the poor prognosis of CVDs in people diagnosed with it. Diabetic patients are highly prone to complications of coronary artery disease, heart failure, stroke, heart attack, and other vascular diseases.
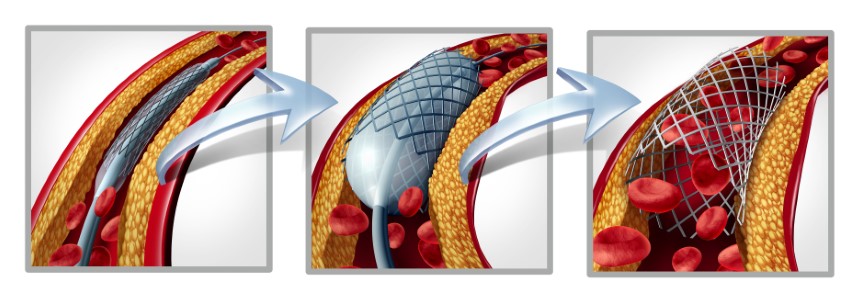
- Link Between Diabetes and CAD There is a strong link between diabetes and CAD. Studies show that diabetic patients are two to four times more likely to develop CAD than non-diabetic patients. In people with diabetes, it is observed that atherosclerosis and atherothrombosis commence early and develop faster, resulting in one of the major reasons for high morbidity and mortality. High triglycerides (body fat) and high LDL (bad) cholesterol cause the arteries to harden, leading to atherosclerosis. The chances of plaque ruptures cannot be ruled out, causing thrombosis and, if unattended, may prove fatal.
- Link Between Diabetes and Heart Attack Diabetes is reported to be responsible for the severe damage to the nerves of the autonomic nervous system. Angina or chest pain is one of the first symptoms of a heart attack. Diabetic patients do not feel chest pain, and heart attack often turn out to be silent.
- Link Between Diabetes and Heart Failure Heart failure is when the heart cannot pump enough oxygen-rich blood efficiently and adequately to meet the body’s blood requirement. It has been studied that diabetes and heart failure have many similar risk factors, and each is an independent risk factor for the other. Diabetes Mellitus has been shown to worsen heart failure due to a rise in serum glucose, glycated hemoglobin levels, and reduced glucose tolerance. Cardiomyopathy (left ventricular dysfunction) is reported to be associated with diabetes, even in the absence of any other valve disease, hypertension, or CAD in diabetic patients. Diabetic patients are at high risk of heart failure, even without any symptoms of heart failure or structural heart disease.
- Gestational Diabetes (GD) and its Associated Risks Women with GD have been reported to have a nearly seven-fold increased risk of developing type 2d in the long run. Diabetes is detrimental to the cardiovascular health of women. The risk of cardiovascular diseases due to diabetes is higher in women than men. This may be attributed to excess weight gain during pregnancy, the more extended period spent in the metabolic prediabetes stage that is unfavorable or placental hormonal effects, or an increase in inflammatory cytokines release during pregnancy causing insulin resistance. Incidence of GD may also affect the health of the baby, who may be born overweight, with chances of obesity or type 2D in the future or breathing problems.
Conclusion
Diabetes is not only chronic but life-challenging, with its devastating effect on the cardiovascular health of the patient. As a silent killer, it stealthily and gradually affects multiple organs and body parts adversely. To prevent any further damage and its aggravating impact on the person’s overall health, one must exercise stringent diabetes control and management measures.
References
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1944600#:~:text=As%20per%20Indian%20Council%20of,of%20diabetes%20is%2010.1%20crores.
https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/silent-heart-attacks-diabetes
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes#:~:text=Over%20time%2C%20diabetes%20can%20damage,blood%20vessels%20in%20the%20eyes.