Are you tired of that nagging hip pain that seems to follow you everywhere you go? Do simple tasks like walking or climbing stairs feel like daunting challenges? If you find yourself nodding in agreement, you are not alone. Many individuals around the globe struggle with debilitating hip conditions that can severely impact their quality of life. However, there is a ray of hope in the form of Total Hip Replacement (THR) surgery. This transformative medical procedure has been a saviour for countless people, offering them relief from chronic pain and the gift of restored mobility. This article will be a guide that will elaborate on the preparation and recovery of Total Hip Replacement, providing invaluable insights on what to expect.
What is Total Hip Replacement?
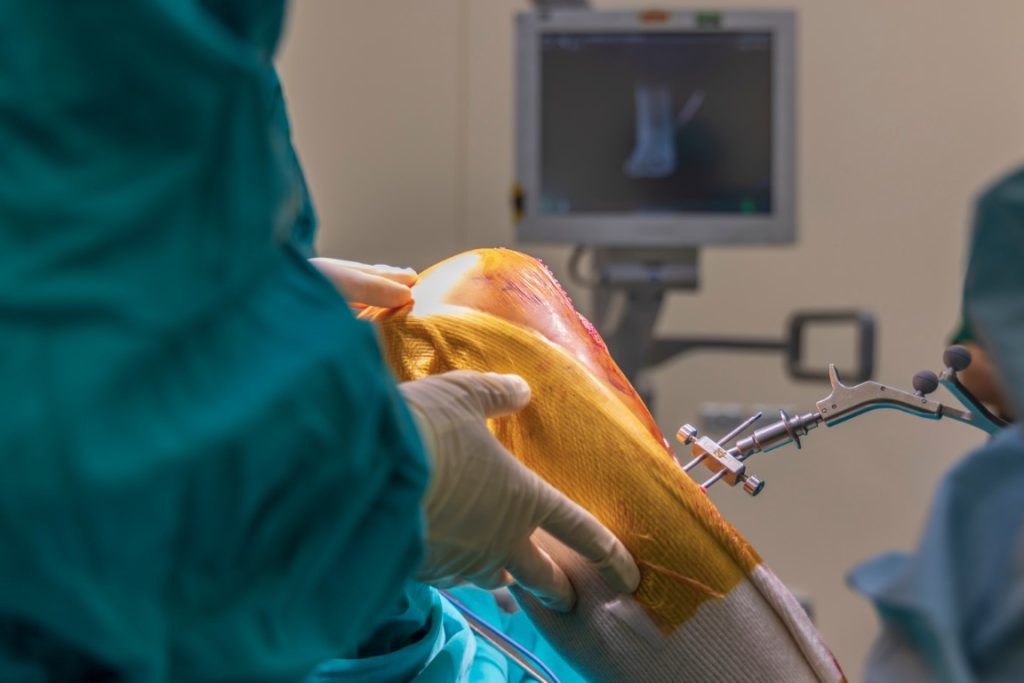
Total Hip Replacement (THR) is also known as hip arthroplasty. THR is a surgical procedure in which a damaged hip joint is replaced with a prosthesis or an artificial joint. The primary purpose of THR is to alleviate pain, improve joint function, and enhance overall mobility. The surgery can be performed on individuals suffering from various hip conditions, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, hip fractures, and other degenerative joint diseases. As one of the most successful orthopaedic surgeries, THR has offered relief and enhanced mobility to millions of Indians.
Total Hip Replacement (THR) surgery is often considered when other non-surgical treatments, like medication and physical therapy, fail to provide sufficient relief. The treatment offers numerous benefits to patients:
- It significantly reduces pain, enabling individuals to engage in daily activities comfortably.
- The procedure restores joint function, leading to improved mobility and flexibility.
- THR enhances the overall quality of life, allowing patients to regain their independence and participate in activities they once enjoyed.
Steps to Undertake Prior to Opting for Total Hip Replacement Surgery
A. Initial Consultation with an Orthopaedic Surgeon
The journey towards total hip replacement begins with an initial consultation with an orthopaedic surgeon. During this visit, the surgeon will thoroughly examine the patient’s hip, assess their medical history, and discuss their symptoms and concerns. The surgeon will also explain the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes. It is essential for patients to be open about their symptoms and expectations to ensure the best possible treatment plan.
B. Medical Evaluation and Diagnostic Tests
Following the initial consultation, a comprehensive medical evaluation will be conducted. This evaluation may include blood tests, X-rays, MRI scans, and other diagnostic tests to assess the hip joint’s condition and the patient’s overall health. These tests are crucial in determining the best course of action and identifying any potential issues that need to be addressed before surgery.
C. Discussing Medical History and Current Medications
Patients must provide their complete medical history to the surgical team. This includes details of any past surgeries, allergies, chronic medical conditions, and current medications. Some medications may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped before the surgery in order to reduce the risk of complications.
D. Addressing Concerns and Questions about the Surgery
It is natural for patients to have concerns and questions about total hip replacement surgery. The surgical team is there to address these concerns and provide the necessary information to ease any anxieties. Clear communication between the patient and the medical team is vital to ensure a smooth and successful surgery.
Pre-Surgery Preparations
A. Lifestyle Adjustments Before Surgery
In the weeks prior to the surgery, patients may be advised to make some lifestyle adjustments to improve their overall health and prepare for the procedure. This might include maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in low-impact exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles, and quitting smoking if applicable.
B. Stopping or Adjusting Medications as Advised by the Doctor
The doctor may advise stopping or adjusting certain medications before the surgery based on the medical evaluation and the patient’s current medications. This is done to minimize the risk of complications and ensure a safe procedure.
C. Planning for Post-surgery Recovery and Support
It is essential to plan for the post-surgery recovery period in advance. Patients should arrange for a support system that may include family members, friends, or home care assistance during the initial days or weeks after the surgery. Preparing the home environment to accommodate mobility aids, such as walkers or crutches, is also recommended.
D. Final Instructions from the Medical Team
The day before the scheduled surgery, the medical team will provide final instructions to the patient. These instructions may include fasting guidelines, specific guidelines on medications to take (if any), and arrival time at the hospital or surgical centre.
E. Pre-surgery Fasting and Guidelines
Fasting is typically required before the surgery to prevent any potential complications during anaesthesia. The medical team will provide clear instructions for stopping eating and drinking before the scheduled surgery.


Recovery and Rehabilitation
Post-surgery recovery in the hospital typically lasts for a few days and involves close monitoring by the medical team to ensure healing, and manage pain. Effective pain management, including medication and techniques, and proper wound care to prevent infection are crucial during this period. Physical therapy is introduced to improve strength, flexibility, and joint mobility, accelerating overall recovery progress.
Conclusion
Total Hip Replacement Surgery is a transformative procedure that offers renewed hope to individuals suffering from debilitating hip conditions. By understanding the process and adequately preparing for the surgery, patients can look forward to an improved quality of life and increased mobility. Remember to communicate openly with the medical team, adhere to pre-operative and post-operative guidelines, and actively engage in rehabilitation to make the most of this life-changing procedure.
FAQs
Q: What can I expect on the day before Total Hip Replacement surgery?
A: The day before the scheduled surgery, you will receive final instructions from the medical team. This will include fasting guidelines, specific guidelines on medications to take (if any), and the designated arrival time at the hospital or surgical centre. Following these instructions diligently is crucial for a smooth and safe procedure.
Q: What is the recovery process like after Total Hip Replacement surgery?
A: After the surgery, you will spend a few days in the hospital for post-operative care and monitoring. The medical team will manage your pain and ensure proper wound care. Early rehabilitation will begin, including physical therapy and mobility exercises to improve strength and flexibility. Your active participation in rehabilitation will significantly impact your overall recovery progress.
Q: How long does it take to resume normal activities after Total Hip Replacement surgery?
A: The time it takes to resume normal activities varies from person to person and depends on several factors, such as the individual’s overall health, adherence to post-operative instructions, and commitment to rehabilitation. While some patients may begin to walk with assistance soon after the surgery, it can take several weeks to months to fully recover and return to regular activities. It’s essential to follow your doctor’s guidance and gradually progress through the rehabilitation process to achieve the best possible outcome.