Do you find yourself wincing with every step, burdened by chronic knee pain that seems to linger endlessly? Chronic knee pain is a common yet challenging condition that affects countless Indians, hindering their ability to enjoy life to the fullest. Dealing with chronic knee pain can be overwhelming, and the quest for relief can be exhausting. However, navigating through a vast sea of healthcare options is crucial, with each alternative promising a path to comfort and mobility. This article will uncover the essential factors to consider while seeking the medical advice for your chronic knee pain. So, let’s lace up our boots and take the first step towards a brighter, pain-free future!
How to Identify Chronic Knee Pain?
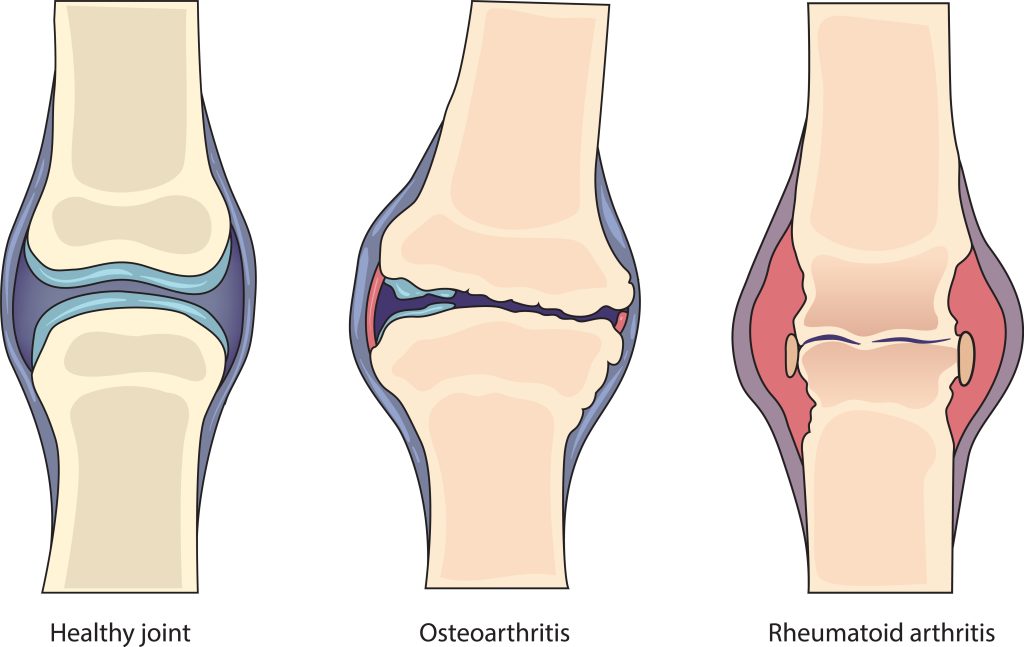
Before delving into the factors to consider, it is crucial to accurately identify chronic knee pain. Chronic knee pain is characterised by persistent discomfort that lasts for an extended period, typically more than three months. It may involve swelling, stiffness, limited range of motion, and difficulty in performing everyday activities like walking or climbing stairs. If you experience such symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical advice promptly.
Factors to Consider For Medical Advice
A. Experience and Specialisation of the Healthcare Provider
When seeking medical advice for chronic knee pain, the experience and specialisation of the healthcare provider play a vital role. Look for orthopaedic specialists, rheumatologists, or sports medicine doctors who have expertise in dealing with knee-related issues. Experienced professionals are better equipped to diagnose the root cause of your knee pain accurately and recommend appropriate treatment plans.
B. Reputation and Patient Reviews of the Medical Professional
In the digital age, accessing information about medical professionals has become easier. Take advantage of patient reviews and testimonials to gain insights into the reputation of the healthcare provider. Positive reviews from patients who have undergone similar treatments can instil confidence in their abilities. However, always remember that individual experiences may vary, so consider a range of opinions before making a decision.
C. Hospital or Clinic Facilities and Resources Available
The facilities and resources available at the hospital or clinic can significantly impact the quality of care you receive. Advanced imaging technology, well-equipped rehabilitation centres, and access to specialists can contribute to better treatment outcomes. Prioritise institutions with a focus on patient-centric care and a comprehensive approach to knee pain management.



Understanding Treatment Options
A. Non-surgical Approaches
Non-surgical approaches are often the first line of treatment for chronic knee pain. These may include physical therapy to strengthen the knee muscles and improve flexibility. Physical therapy can also help in correcting any gait abnormalities that might be contributing to the pain. Additionally, medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs or pain relievers might be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve daily function.
B. Surgical Interventions
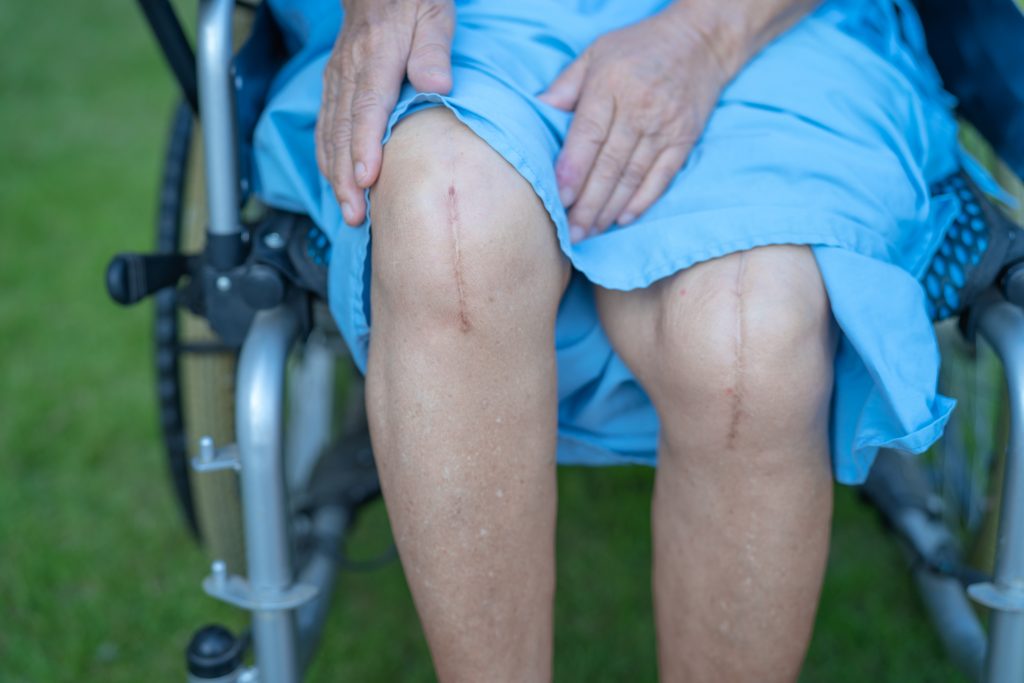
Surgical interventions may be considered if non-surgical treatments do not provide adequate relief. Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure, is often used to diagnose and treat various knee conditions. During arthroscopy, the surgeon inserts a tiny camera into the knee joint to view and repair any damage. In more severe cases, knee replacement surgery might be recommended. Knee replacement involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
C. Benefits of Each Treatment Option
Each treatment option has its benefits, and the choice depends on the severity of the knee condition and the individual’s overall health. Non-surgical approaches are generally less invasive, have shorter recovery times, and are suitable for mild to moderate knee issues. On the other hand, surgical interventions can provide more significant and long-lasting relief for severe cases of chronic knee pain. It is crucial to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each option with your healthcare provider to make an informed decision.
Managing Expectations and Realistic Goals
Set realistic expectations for treatment outcomes. Understand that individual responses vary, and complete pain relief may not always be possible. Discuss the prognosis and expected results with your healthcare provider to prepare for the journey ahead.
Acknowledge possible limitations in treatments and the significance of post-treatment care. Lifestyle adjustments, ongoing physical therapy, or regular follow-ups might be necessary. Adhere to post-treatment care for optimal results and to prevent future complications.
Conclusion
Dealing with chronic knee pain requires careful consideration when seeking medical advice. Evaluating the experience and specialisation of the healthcare provider, reviewing patient testimonials, and considering the facilities available are crucial steps in making an informed decision. Understanding the available treatment options and their benefits and managing expectations will contribute to a more effective treatment journey.
FAQs
Q: What should I look for when seeking medical advice for chronic knee pain?
A: When seeking medical advice for chronic knee pain, consider the experience and specialisation of the healthcare provider. Look for orthopaedic specialists, rheumatologists, or sports medicine doctors who have expertise in dealing with knee-related issues. Additionally, review patient testimonials and the reputation of the medical professional to gauge their effectiveness in managing knee pain. Don’t forget to assess the facilities and resources available at the hospital or clinic to ensure comprehensive care.
Q: Are there non-surgical options for managing chronic knee pain?
A: Yes, there are non-surgical approaches for managing chronic knee pain. These may include physical therapy to strengthen the knee muscles and improve flexibility. Physical therapy can also help correct any gait abnormalities that contribute to the pain. In some cases, medications might be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve daily function.
Q: How can I manage my expectations regarding treatment outcomes?
A: Managing expectations is crucial when dealing with chronic knee pain. It’s essential to have open and honest discussions with your healthcare provider about the prognosis and expected outcomes of the chosen treatment plan. Keep in mind that individual responses to treatments may vary, and complete pain relief might not always be possible. Understanding potential outcomes will help you prepare mentally and emotionally for the treatment journey.
Q: What role does post-treatment care play in managing chronic knee pain?
A: Post-treatment care is vital for optimising treatment results and preventing future complications. Depending on the chosen treatment option, you might need to follow lifestyle modifications, participate in ongoing physical therapy, or attend regular follow-up appointments. Adhering to post-treatment care recommendations will aid in your recovery and support your journey towards a pain-free and active lifestyle.