The process of pregnancy is both a wonderful one, as well as one that is filled with doubts and questions. The moment someone finds out they are set to be a parent, the health of both the mother as well as the child becomes equally important.
Most often than not, pregnancies occur without any complications. But, certain pregnant women will encounter complications, affecting them or their baby’s health. In some cases, chronic disorders in expecting mothers, occurring before becoming pregnant, are responsible for causing complications during pregnancy. Some events also occur at the time of delivery. Early diagnosis and prenatal caution can minimize further risk to you and your baby even with complications.
What are these complications?
Pregnancy symptoms and complications can range from mild discomforts to severe, sometimes life-threatening illnesses. It can be difficult for a mother to determine which symptoms are normal and which are not. Problems during pregnancy may include physical and mental conditions that affect the health of the mother or the baby. Hence, proper precaution and doctor’s guidance is mandatory. Some of the most frequent complications of pregnancy include:
- Hypertension or high blood pressure:
High blood pressure, also called hypertension, occurs when arteries carrying blood from the heart to the body organs and the placenta are narrowed. During pregnancy, this can make it difficult for blood to reach the placenta, which provides oxygen and nutrients to the fetus. It also puts the mother at a higher risk of having a baby well before their due date. When such a premature delivery takes place, it is called a preterm delivery.



- Gestational diabetes:
At times, when a woman is pregnant, her body may not be able to process sugar effectively. This leads to higher-than-normal levels of sugar in their bloodstream. When such a thing happens, a woman may contract gestational diabetes. But even if it occurs, it should not be a big worry because gestational diabetes usually gets resolved after pregnancy. Still, it can cause problems during pregnancy, so women need to keep an eye out for it.
- Pre-eclampsia:
When pregnant, it is pertinent a woman gets herself checked for Pre-eclampsia, which is also known as Toxemia. This condition generally occurs after the initial 20 weeks of pregnancy, and when it does, it causes symptoms such as hypertension or problems with the kidney. While Pre-eclampsia can lead to outcomes like preterm delivery, in some serious cases, it can even cause fatalities, so you must consult with your doctor and stay completely clear of it.



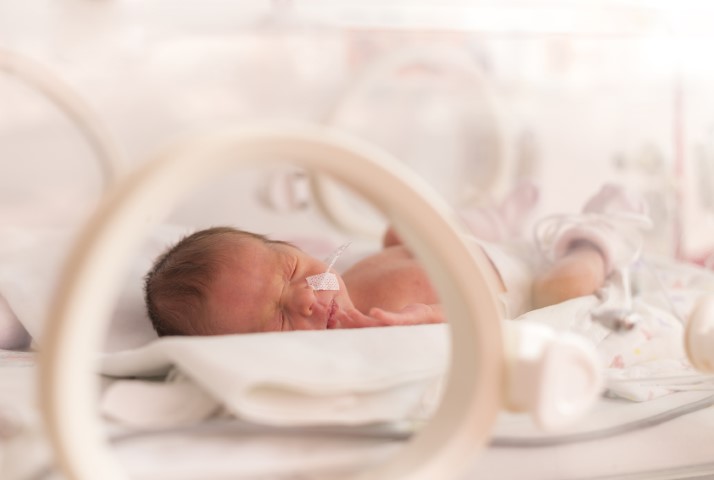
- Pre-term Labour:
At times, a woman may go into labor much earlier than expected. Ideally, 37 weeks is what can be considered normal delivery time, and anything before it can be called preterm. Preterm delivery can put the infant at higher risk because certain organs like the brain and lungs may not have completely developed as yet. At such times, the infant may need to be put in an incubator or an intensive care unit for a while, till it develops fully functioning organs.
- Miscarriage:
A miscarriage is the loss of a pregnancy during the first 20 weeks due to natural causes. Signs can include cramping, vaginal bleeding, or fluid or tissue passing from the vagina. It is recommended to contact your health care provider if you experience these signs at any point during pregnancy.



- Stillbirth:
The loss of an infant after week 20 of pregnancy is called a stillbirth. Mostly, the cause of stillbirth is unknown. However, health conditions that can contribute to stillbirth include problems with the placenta or chronic health issues in the mother that affect the child.
- Anemia:
It is a condition in which a woman has a lower than the normal count of healthy red blood cells. This makes it hard to carry adequate oxygen to the body’s tissues. Having anemia can make pregnant women feel tired and weaker than usual, which may lead to complications when the pregnancy advances.



- Infections:
A variety of viral, bacterial, parasitic or sexually transmitted infections may occur during pregnancy and/or delivery which may lead to complications for the mother and the baby after delivery. Many of these infections can be prevented or treated with appropriate prenatal, pre-pregnancy along with postpartum follow-up care.
- Hyperemesis gravidarum:
Extreme, persistent nausea and vomiting during pregnancy, particularly in the first trimester. Some women may experience more severe symptoms that last into the third trimester. It can lead to weight loss, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances.



- Ectopic Pregnancy:
A pregnancy in which the fertilized egg settles and grows outside the uterus, generally in the fallopian tube. The fertilized egg can’t survive outside the uterus. If left to grow, it may damage nearby organs and cause life-threatening loss of blood.
Can complications also occur during the time of delivery?
When a woman goes into delivery, certain pregnancy-related complications can arise. These include:
- Breech position:
A baby is considered to be in the breech position when it is formed head-up in the mother’s uterus. This means the feet are pointed toward the birth canal and can complicate normal vaginal delivery a bit.
- Placenta previa:
It occurs when a fetus’s placenta partially or covers the mother’s cervix — the outlet for the uterus. It may cause severe bleeding during pregnancy and delivery.
- Low birth weight:
Babies who are born with low birth weight carry an elevated risk of respiratory infections, cardiac infections, learning disabilities or problems with vision.



How can you prevent pregnancy complications?
Not all complications are preventable. Following these guidelines may help promote a healthy pregnancy and lessen the chance of high-risk pregnancy complications.
- Attend doctor’s appointments regularly
- Maintain a healthy diet
- Quit smoking and drinking alcohol
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Take prenatal vitamins daily
- Try Yoga and Meditation to stay fit



In the months of pregnancy, a lot of pregnancy complications can arise, even in healthy women. Most often than not, these health complications shouldn’t deter couples from planning for a child.
While pregnant, along with doctor visits, it is important to keep an eye on vital signs as well as any complications, no matter how small or inconsequential they seem. Stick to a regimen set by your doctor and while it may not resolve all complications, it will improve your chances of having a normal delivery which of course, will ensure your bundle of joy is as healthy as it is supposed to be!