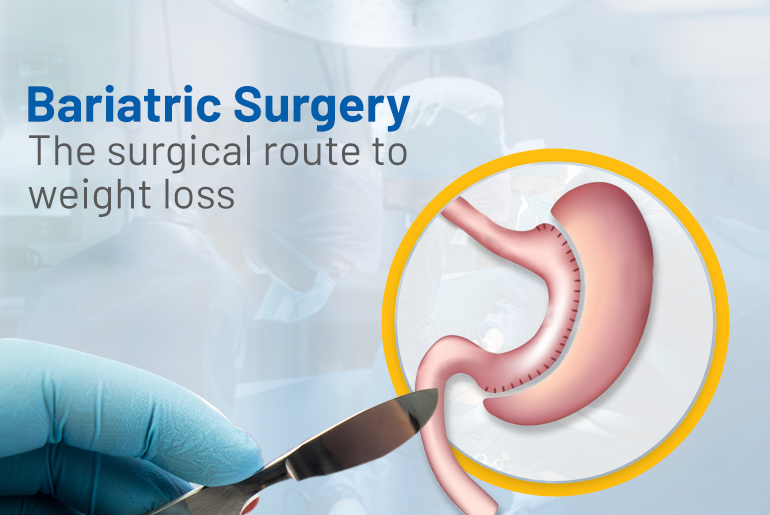
Weight loss surgery also known as or Bariatric or Metabolic surgery are several terms used, interchangeably for patients suffering from Obesity and its health complications. The surgery has become very common and can be truly life-changing for patients. We have to understand that Obesity is a “disease” and not just a cosmetic problem or a character flaw. Someone thinking about the surgery needs to understand the changes in lifestyle that come with the surgery, and the habits one should build to become healthier.
First of all it is really important to know that this is NOT a cosmetic procedure that removes some body fat. This surgery “resets” the GI system of the body. There are different types of Bariatric surgery which are all generally done either Laparoscopically or with Robotic assistance. The surgery works in several ways, including restricting the diet, decreasing the absorption of food and most importantly, the metabolic or hormonal changes that happen with the surgery.
So, in fact, it is a procedure where the effectiveness of the surgery is user dependent. Someone can take great help from the procedure and put it to great benefit for themselves by following the diet, exercise recommendations, losing most of their excess weight and getting rid of diabetes, high blood pressure and several other complications. The surgery can greatly improve not only physical but also mental health. At the same time reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke and several cancers.
So who is the surgery really for?
A 23 year old Male with a strong family history of Obesity started suffering very early in life and got into a vicious circle of weight, poor self esteem and depression with comfort eating and progressive weight gain. He had been trying to lose weight over 2 years with dieting and exercise but after losing 10-12 Kg when things would stall he would give up which became a constant source of frustration for him. After Bariatric surgery he lost 15 kg in one month and was able to easily follow the recommended diet due to reduced hunger. He started exercising vigorously within a month of surgery and took things to the next level with the self-encouragement. Within one year he lost 60 Kg weight going from 150 Kg to 90 Kg and gained significant muscle mass. Exercise became his new passion so much so that it really helped him follow a very strict diet with almost excluding carbohydrates!
A 37 year old female gained significant weight during pregnancy and continued to put on weight later which she found extremely hard to keep off. When she developed diabetes requiring medications at such a young age she resolved to get rid of the excess baggage. Laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery meant that the very next day of surgery her diabetes went into remission and all the medicines were stopped. Within 3 months of surgery she lost 25 Kg weight and felt active enough to resume her job that she had left a year back.
A 55 year old Male started putting on weight in his early 40s due to a desk job with minimal activity and compounded by poor eating habits. He started smoking excessively due to depression creeping in. When at age 53 he suffered a massive heart attack requiring emergency cardiac surgery he got a jolt and a wakeup call. After recovering from the surgery the Cardiologist suggested Bariatric surgery to help reduced his risk factors as he was BMI 47 with hypertension, high cholesterol, and having already suffered a heart attack at a young age. He stopped smoking and a month later consulted for Bariatric surgery to address the burning issue of Morbid obesity. After adequate pre surgery evaluation including a Stress Echo test he underwent the surgery successfully. He lost 45 Kg weight over a year, stopped medicines for high BP and cholesterol. He gradually began exercising almost an hour daily!
A 65-year-old female had avoided her weight issue up until a point where he knees gave up due to severe Osteoarthritis. She was advised to lose 20 Kg weight before a Knee replacement, a task much easier said than done when you can’t walk! Which is when she decided to take the help of Bariatric surgery. Within one year of surgery she lost 25 Kg weight and a year later underwent a successful knee replacement surgery. “I feel 20 years younger and can do things now that I haven’t done for over 10 years!” to put it in her own words.
These are some real-life examples of people who decide to take their life back in their hands and not just underwent surgery but also followed the diet and exercise recommendations afterward with regular follow-up. With the right care, taking proper protein, multivitamin supplements and regular exercise complications can be low. More importantly, the benefits of the surgery far outweigh the risks associated with it. Ultimately one has to themselves make an informed choice for their health!
The blog has been authored by Dr Vikas Singhal, Associate Director- GI and Bariatric Surgery. The content is for informational purposes only and should not be taken as professional medical advice.