Introduction
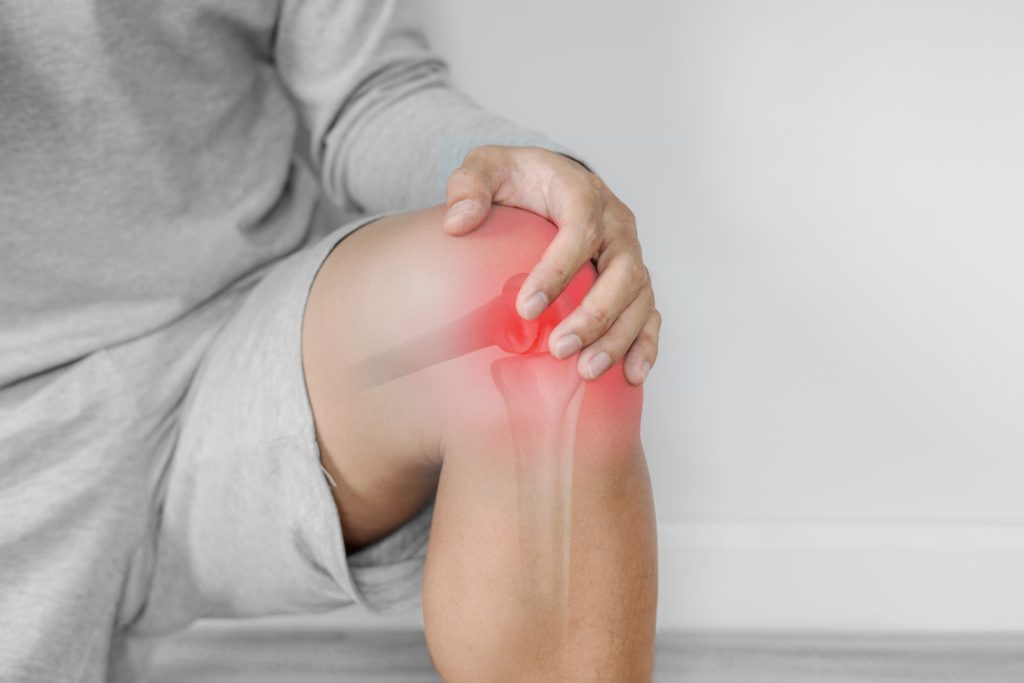
The knee joint is a hinge joint that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). The knee is responsible for a wide range of motions, including flexion and extension, and is one of the most complex joints in the body.
What is Knee Deformity?
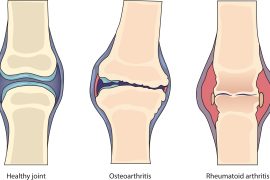
Knee deformity refers to any abnormal shape or alignment of the knee joint. A variety of factors, including genetics, injury, and certain medical conditions, can cause these conditions. While some knee deformities are congenital, meaning they are present at birth, others can develop later in life as a result of injury or other medical conditions. Injury, resulting into a fracture or ligament tears, and conditions like obesity, which can put extra stress on the knee joint can cause knee deformity. Some knee deformities can also cause instability in the knee joint, which can lead to an increased risk of falls and injury. This can be especially problematic for older adults or those with other underlying medical conditions. Osteoarthritis causes knee deformities, which is a degenerative joint disease that can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. This can occur when the abnormal shape or alignment of the knee joint leads to increased wear and tear on the cartilage and other structures in the knee.
Different Kinds of Knee Deformity
Knee deformity could be in form of genu valgum (knock-knee), genu varum (bow-legged), and genu recurvatum (hyperextended knee).
- Genu valgum, or knock-knee, is a condition in which the knees angle outwards and bend inward, touching one another with ankles apart even when a person is standing.
- Genu varum, or bow-legged, is a condition in which the knees angle inwards, causing the ankles to touch while the knees remain apart.
- Genu recurvatum, or hyper-extended knee, is a condition in which the knee joint extends beyond its normal range of motion, causing the knee to bend backward.
How to Treat Knee Deformity
Treatment for knee deformity will vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. It is essential to consult a doctor or physical therapist if you are experiencing pain or difficulty with mobility in your knee. They can help you determine the underlying cause of the deformity and recommend the best course of treatment. With the right treatment and management, most people with knee deformities can live a normal and active life.
Physical therapy can help to improve strength and flexibility in the knee, which can help to alleviate pain and improve mobility. Regular exercise can also play a key role in managing knee deformity by improving strength, flexibility, and mobility in the knee. A physical therapist can help develop an exercise plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Surgery may be necessary in severe cases to correct the deformity and restore normal function to the knee. Surgery for knee deformity can include procedures such as osteotomy, which involves cutting and repositioning the bone to correct the deformity, or arthroplasty, which involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one. The choice of surgery will depend on the specific condition and the severity of the deformity.
In addition to physical therapy, bracing, and surgery, other treatments for knee deformity include the use of assistive devices such as crutches or a knee brace and medications to manage pain and inflammation. Bracing can be used to help support the knee and prevent further deformity.
Conclusion
It is important to note that knee deformities can be progressive, meaning they can worsen over time. It is essential to seek medical attention early to prevent further deterioration and improve the chances of a successful outcome with treatment. A medical professional can only make an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan after a thorough examination.
FAQs
Q: What causes knee deformities?
A: Knee deformities can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, injury, and certain medical conditions such as Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ligament or cartilage tears, and congenital conditions.
Q: Are knee deformities serious?
A: In most cases, knee deformities are not serious and do not require treatment. However, if a deformity is causing pain or difficulty with mobility, it can affect day to day activity.
Q: How are knee deformities treated?
A: Treatment for knee deformities will vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Treatment options include physical therapy, bracing, surgery, the use of assistive devices, and medications to manage pain and inflammation.
Q: Can knee deformities be prevented?
A: Some knee deformities, such as those caused by genetics or congenital conditions, cannot be prevented. However, other deformities can be prevented by taking measures to protect the knee joint, such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding injury, and staying active.
Q: Can knee deformities be cured?
A: The treatment of knee deformities can help to alleviate symptoms and improve mobility, but it may not always result in a complete cure.
Q: How can I manage knee deformity?
A: In addition to medical treatment, regular exercise can play a key role in managing knee deformity by improving strength, flexibility, and mobility in the knee. A physical therapist can help develop an exercise plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
References :
https://www.kneeandshoulderclinic.com/knee-deformities.html

Comments are closed.