Introduction
Many of you must have experienced that typical sensation triggering a varied range of pain in the parts of your head. The pain creates inconvenience, stress, and discomfort, hampers the routine, and makes daily activities challenging. This pain in the head and face area is termed a headache. The pain may be in different parts of the head with varying duration and symptoms. Headaches are common, and some people are more prone than others. However, its frequency and associated symptoms must be monitored to prevent them from worsening to severe health conditions.
Headaches may result from environmental changes or routine changes, like exposure to excessive noise, heat, or fast observation. Sometimes, they may be the symptom of underlying disease, as in the case of sinusitis. The cause of headaches could be different. The difference in the type of headaches must be understood to treat it effectively and timely.
The present blog discusses sinus headaches, how they are different from other headaches and their treatment options to enable readers to make informed decisions about treating specific types of headaches effectively.
Types of Headache
The throbbing pain of headaches is known to many; its severity, symptoms, and treatment may differ depending on its type. The different types of headaches are –
- Migraine headache is a reoccurring headache with pain on one side. It often comes with blurry vision, heightened sensitivity to light and sound, or nausea and vomiting.
- Tension headaches are often caused by stress, tension, and anxiety with symptoms of pain, tenderness in the head, face, and neck, and sensitivity to light and/or sound.
- Cluster headache is a severe and recurring headache, with symptoms of watery eyes, blocked nose, and swelling eyelids.
- Hormone headache is also known as menstrual headache and is caused in women due to hormonal changes.
- Sinus headache is caused by an infection in the sinuses.
- Hypnic headache usually occurs in old age with no specific cause identified.
- Rebound headache is a secondary type of headache caused by overuse of medications. It may subside with medication but reoccurs.
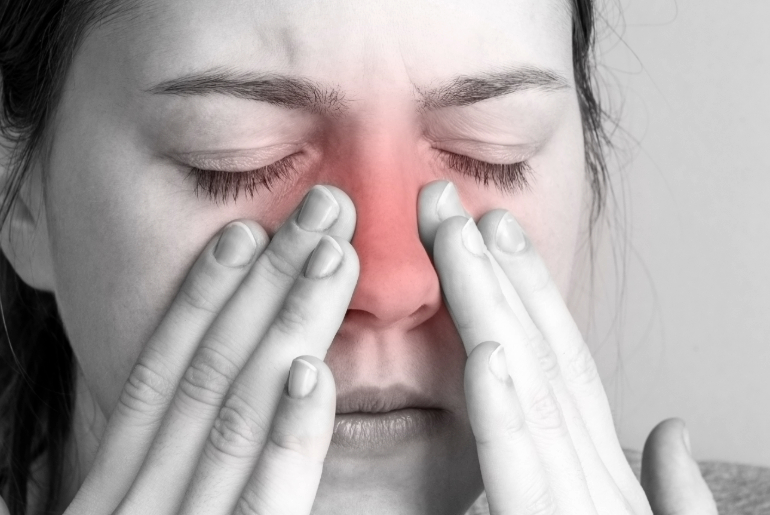
What is a sinus headache?
A sinus headache is caused when the sinuses get inflamed and blocked due to infection and cannot drain the mucus from the nasal passage. The resultant pressure in the sinuses causes pain in the head. A sinus is a space inside the forehead, cheeks, and behind the nose. The space is filled with air, which helps drain the mucus, keeping the nasal passage clear from bacteria and other types of infection. The condition of infection and inflammation in the tissue lining of the sinuses is known as sinusitis. Sinusitis is caused by viruses, bacteria, allergens, or fungi infection.
How is sinus headache different from other types of headaches?
Headaches due to sinuses are often mistaken for other types of headaches like migraine, tension headaches, and hypnic headaches, to name a few. However, the cause, symptoms, severity, and duration of the headache help determine the type of headache.
- Sinus headaches and migraines are often confused due to shared symptoms like watery eyes, pressure on the face, congestion, pain while bending forward, or runny nose. Migraine causes pain on one side of the temple, eyes, and back of the forehead. It is associated with sensitivity to loud noise, bright lights, nausea, and vomiting. The pain lasts for hours or a day or two.
- Similarly, tension headaches caused by stress, fatigue, anxiety, and exposure to sound last for a few hours. The pain is felt in the entire head and is mild or moderate. It affects the back of the head, the neck, and both sides.
- The rebound headache caused by overuse of medications is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, restlessness, loss of memory, and irritability. Pain-relieving medications help relieve the pain for the time being, and the headache rebounds when its effect is gone. The overuse of pain relievers triggers headaches.
- On the other hand, a sinus headache caused by infection is followed by fever. It causes thick discoloration of mucus discharge, cough, pain in the cheeks and teeth, or loss or decrease in sense of smell. It lasts for days or weeks, depending on the type of sinusitis.
How to treat a sinus headache?
The treatment options for each type of headache are different and unique. One must avoid trying to treat one type of headache with the treatment option of the other and prevent its worsening.
Sinus headaches must be treated with an effective diagnosis of the underlying causes and symptoms through allergy tests, X-rays or CT scans. Risk factors like allergies, colds, exposure to smoking, weakened immune system, and structural nasal deformity need to be understood and addressed. The treatment starts with home remedies to relieve the pain, which include nasal sprays, steam inhalation or use of vaporizers, and the application of warm compressors to relieve swelling or pain in the affected areas.
Medications like antihistamines that prevent allergies, decongestants for reducing swelling, steroids for reducing inflammation, and pain medicines for pain relief help control the pain and discomfort of sinus headaches.
Generally, sinuses go on their own or with the help of medications. Still, in cases of severe and long-lasting symptoms of sinusitis, the doctor may recommend sinus surgery.
- FESS- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery- FESS is a simple and standard surgical treatment option for unhealthy sinuses. The surgery involves widening the nasal passages between the nose and the sinuses to remove the infected bone or tissues obstructing the drainage of the mucus.
- Balloon Sinus Ostial Dilation- Balloon sinuplasty drains the mucus and relieves the patient of sinus symptoms using a balloon placed at the tip of the flexible catheter. When the catheter reaches the correct position, the balloon is inflated to open and widen the sinus cavities, and the mucus gets flushed out. The procedure does not require incisions as it is done through the nostrils.
- Turbinate Reduction- During turbinate (a small bony structure inside the nose) surgery, the surgeon reduces the turbinate size with a needle-like instrument inserted inside the nose.
Conclusion
Sinus headaches are signs of sinus infection. They differ from other types of headaches regarding their causes, symptoms, severity, and duration. These headaches could be challenging and affect the patient’s quality of life. Most cases, the symptoms may go away with home remedies or medications. Still, in severe cases, surgical intervention might be needed. Never take frequent headaches lightly, for they may develop into worsening conditions. Timely medical attention and assessment are necessary for effectively treating sinus headaches.