Introduction
Are you familiar with the surgical procedure known as laparotomy? It may not be a household term, but it’s a critical procedure to diagnose and treat various medical conditions. From abdominal trauma to digestive disorders, laparotomy can make all the difference in a patient’s recovery. But what exactly is laparotomy, and when is it needed? In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of laparotomy, from the procedure to the recovery process.
What Is Laparotomy?
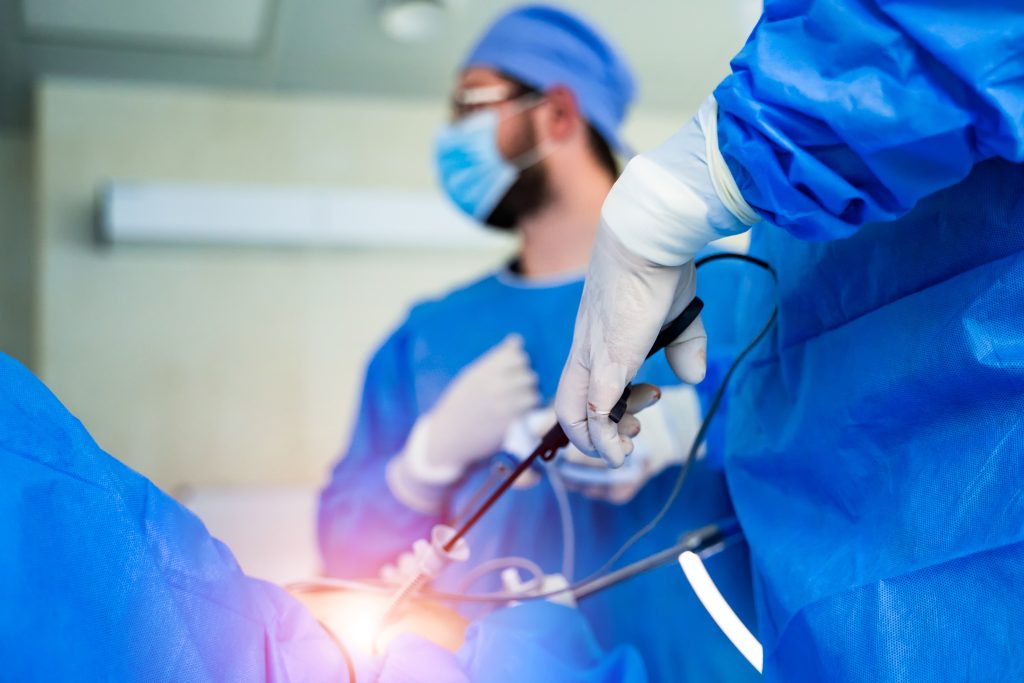
Also known as open abdominal surgery, laparotomy is an invasive procedure requiring high skill and expertise. It is a surgical procedure involving an incision in the abdomen to access the internal organs. Doctors can access the organs and tissues and identify abnormalities or issues causing symptoms. Laparotomy may be necessary for trauma, tumours, infections, and digestive disorders.
In addition to its diagnostic capabilities, laparotomy can also be used to treat various medical conditions. For example, a surgeon may remove a tumour or cyst during laparotomy or repair damage caused by trauma. By addressing these issues directly, patients can often experience relief from their symptoms and a better overall quality of life.
Which Medical Conditions Require Laparotomy?
Some of the medical conditions that require laparotomy include:
- Tumours: To remove tumours (cancerous or non-cancerous) located in the abdomen.
- Intestinal blockages: To remove a blockage in the intestine that is causing severe abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Ectopic pregnancy: To terminate a pregnancy that is located outside of the uterus, which can be life-threatening.
- Trauma: To treat internal injuries resulting from trauma, such as those caused by accident.
Laparotomy Procedure
The laparotomy procedure is performed under general anesthesia, meaning you will be asleep. The procedure typically takes several hours and is performed in a sterile operating room.
- Preparation for Laparotomy: Before the procedure, you must fast for several hours to ensure your stomach is empty. You may be given laxatives to clean your bowels, antibiotics to prevent infection, and medication to prevent blood clots.
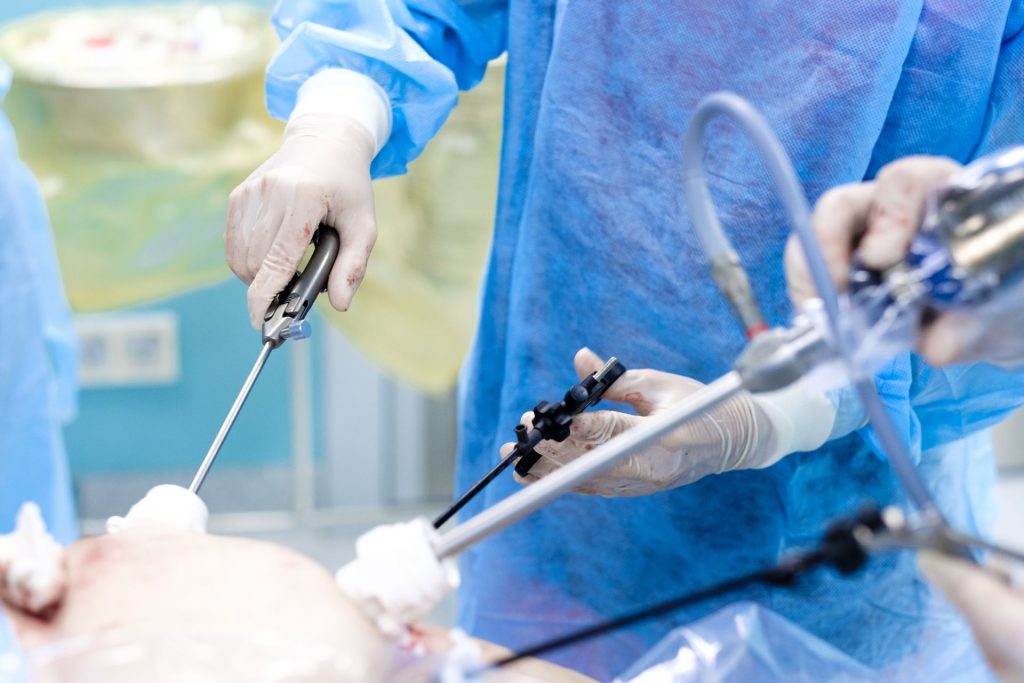
- Exploration and Surgery: During the laparotomy procedure, the surgeon will make an incision in your abdomen. The surgeon will then explore the abdominal cavity to identify any medical conditions that require treatment. If a medical condition is identified, the surgeon will perform the necessary surgery to remove or repair the affected area.
- Closing the Incision:After the surgery, the surgeon will close the incision using stitches or staples. A sterile dressing will be applied to the incision to prevent infection. You will then be taken to a recovery room, where you will be closely monitored as you wake up from anesthesia.
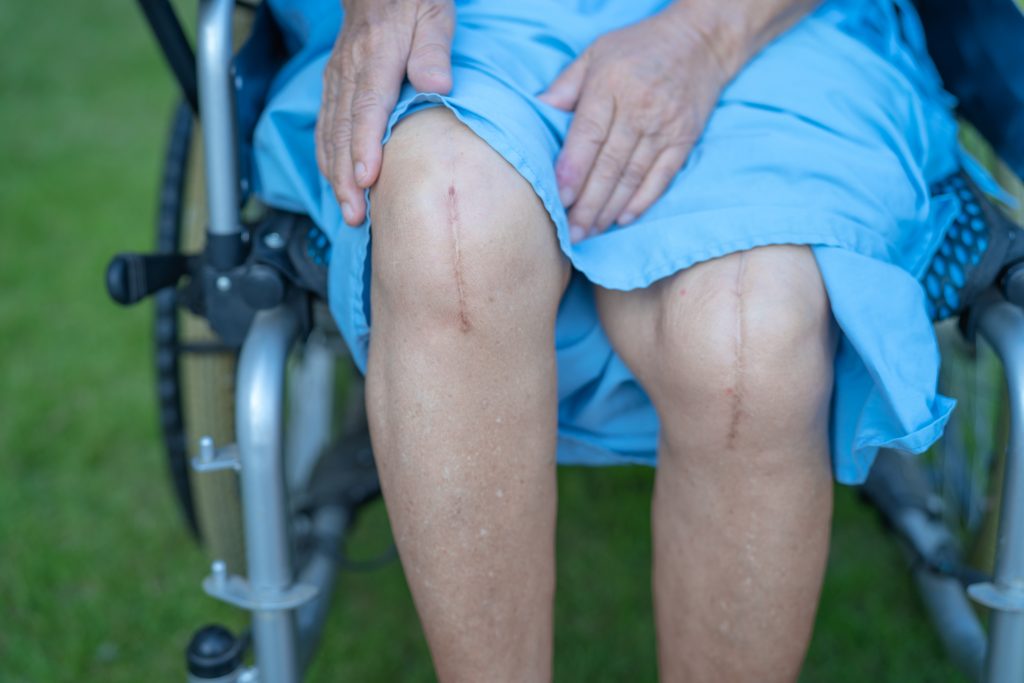
Recovery after Laparotomy
- Hospital stay and aftercare: After laparotomy, you will need to stay in the hospital for a few days to a week, depending upon the requirement of immediate aftercare for proper recovery. During this time, medical staff will monitor you closely, and you will have several tests to guarantee no complications.
- Pain management and medication: Post-laparotomy, you will experience pain and discomfort. Your doctor will provide you with pain medication to help manage your pain. Taking your medication as prescribed is crucial to ensure you are comfortable and prevent complications.
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation: You may need physical therapy and rehabilitation to regain strength and mobility. Your doctor will develop a plan tailored to your specific needs. However, following the plan ensures you recover fully and quickly.
- Follow-up appointments: Once discharged from the hospital, you must attend follow-up appointments with your doctor. These appointments will allow them to monitor your progress and ensure that you are recovering properly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, laparotomy is a critical surgical procedure to diagnose and treat various medical conditions. From abdominal trauma to tumours and infections, laparotomy can help doctors better understand the internal complications of the body and provide targeted treatment to the affected area. While recovery may involve discomfort and rehabilitation, following your doctor’s instructions carefully is essential to ensure a full and speedy recovery. With early diagnosis and treatment, you can improve your chances of a successful outcome and return to your daily life as quickly as possible.
FAQs
Q: What medical conditions typically require laparotomy?
A: Laparotomy may be necessary to diagnose or treat various conditions, including abdominal trauma, tumours, abdominal infections, digestive disorders, and more.
Q: How can I tell if I need a laparotomy?
A: If you are experiencing symptoms of a medical condition that may require laparotomy, such as severe abdominal pain, fever, or vomiting, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Your doctor can evaluate your symptoms and determine if laparotomy is necessary.
Q: How can I prepare for a laparotomy?
A: Your doctor will provide you with detailed instructions on how to prepare for laparotomy. This may involve fasting for some time before the procedure and abstaining from certain medications or supplements.
Q: What is the recovery process like after laparotomy?
A: Recovery after laparotomy may involve pain management, physical therapy, and rehabilitation. You might need to stay in the hospital for a few days to a week, depending upon the need for immediate aftercare for proper recovery. You must attend follow-up appointments with your doctor to ensure you are recovering properly.
Reference links –
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/laparotomy
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/24767-laparotomy
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/laparotomy