What Happens After an IUD Insertion?
So, you’ve decided to get an intrauterine device (IUD). Maybe you’re a bit nervous, or perhaps you’re just curious about what comes next. You’re not alone—many women have the same questions. What exactly happens after an IUD insertion? Is it painful? Will it affect your daily activities? Find the answer to all your questions in our detailed guide.
Immediate Post-Insertion Experience[1]
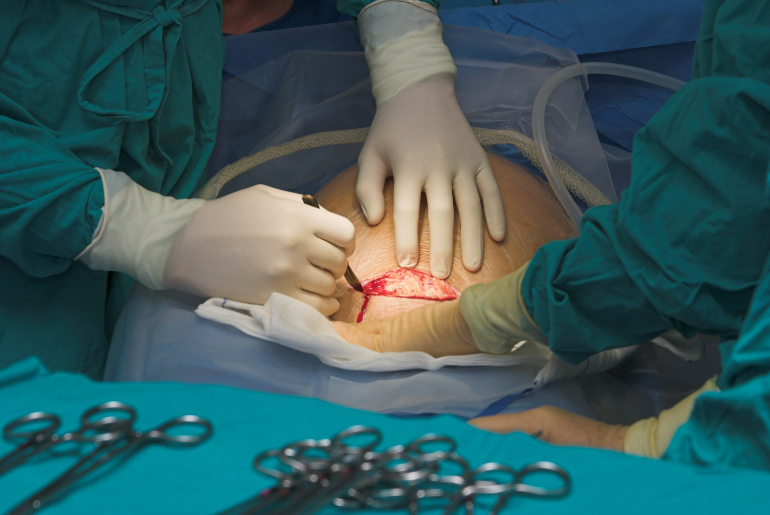
An IUD insertion is usually a quick procedure performed in a healthcare provider’s office. The process involves placing a small, T-shaped device into the uterus through the cervix. While the insertion itself is relatively fast, typically taking just a few minutes, the sensations you feel during and immediately after can vary.
An IUD insertion is usually a quick procedure performed in a healthcare provider’s office. The process involves placing a small, T-shaped device into the uterus through the cervix. While the insertion itself is relatively fast, typically taking just a few minutes, the sensations you feel during and immediately after can vary.
Short-Term Side Effects[1]
You may notice a few short-term side effects in the days following your IUD insertion. These are generally mild and should improve over time.
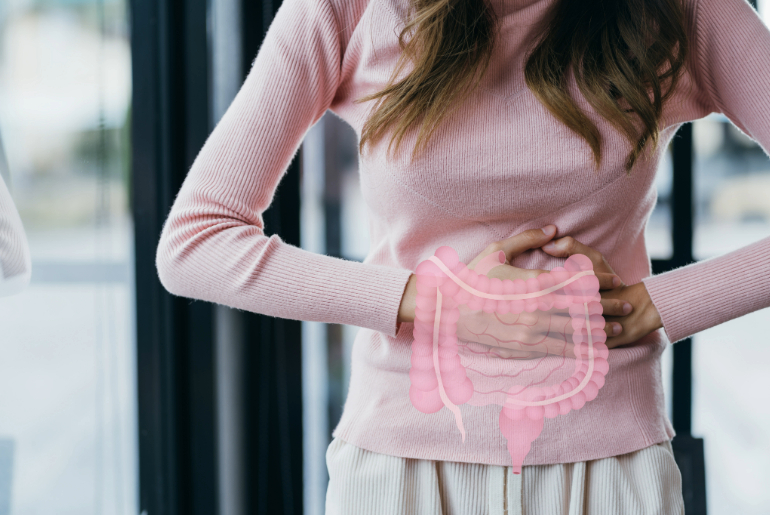
Cramping: It’s common to experience cramping similar to menstrual cramps after an IUD insertion. These cramps can vary in intensity but usually subside within a few days.
Spotting or Light Bleeding: You might experience spotting or light bleeding for a few days to weeks after the procedure. This is a normal response as your body adjusts to the presence of the IUD.
Adjusting to the IUD[1]
Your body may take a few months to fully adjust to the IUD. During this adjustment period, you might notice changes in your menstrual cycle.
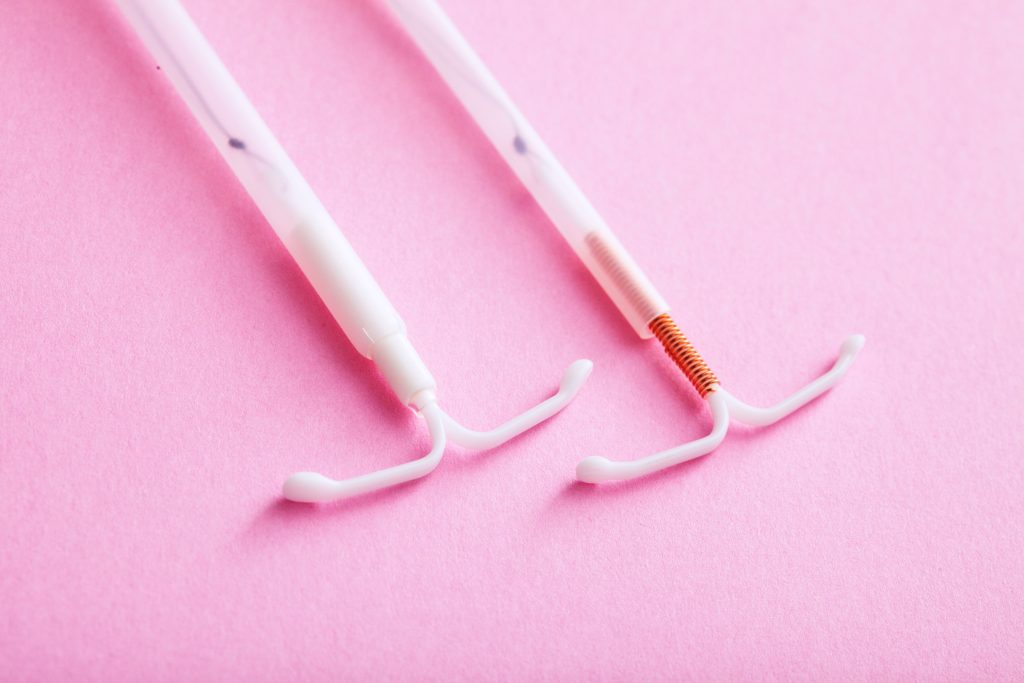
Copper IUD: If you have a copper IUD, you may experience heavier periods and increased cramping. These symptoms often improve after the first few months.
Hormonal IUD: With a hormonal IUD, you might notice lighter periods, irregular bleeding, or even the absence of periods altogether. These changes are common and usually stabilize after a few months.
When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider[2]
Severe Pain or Cramping: If you experience severe pain or cramping that does not improve with over-the-counter pain relief, it’s important to seek medical attention.
Heavy Bleeding or Unusual Discharge: Heavy bleeding or unusual discharge can be a sign of a complication and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Signs of Infection: Symptoms such as fever, chills, or foul-smelling discharge may indicate an infection and require prompt medical attention.
IUD String Issues: If the IUD string feels shorter or longer than usual, or if you cannot feel it at all, contact your healthcare provider. This could indicate that the IUD has shifted.
Suspected Pregnancy: Although rare, pregnancy can occur with an IUD. If you suspect you might be pregnant, it’s crucial to see a healthcare provider immediately.
Lifestyle and Daily Activities
After your IUD insertion, you can generally resume most of your normal activities right away. However, there are a few precautions to keep in mind:
Avoid Insertions[3] : It’s recommended to avoid inserting tampons or engaging in intercourse for at least 24 hours post-insertion to reduce the risk of infection.
Gentle Exercise[4] : Engaging in gentle exercise and activities is encouraged, but you might want to avoid intense physical exertion initially, as it could worsen cramping.
Sexual Activity
It’s important to regularly check the IUD strings to ensure the device remains in place, especially before engaging in sexual activity. This simple check can help you feel more confident that your IUD is correctly positioned and functioning as intended.
Conclusion
Understanding what happens after an IUD insertion can help you feel more prepared and at ease with the process. With proper care and attention, an IUD can be a highly effective and convenient method of contraception.
Reference Links: