Aortic stenosis (AS) is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition affecting millions worldwide. While the condition can develop slowly over time, it can quickly become a major health concern, if left untreated or caught late, AS can progress rapidly and cause massive organ damage, leading to congestive heart failure and death within weeks or even days.
That is why knowing the causes and symptoms of AS is crucial to understand the severity of the condition and catching it early before it gets out of hand. So read on to learn more about this condition and how to protect yourself from its potentially life-ending consequences.
What is Aortic Stenosis?
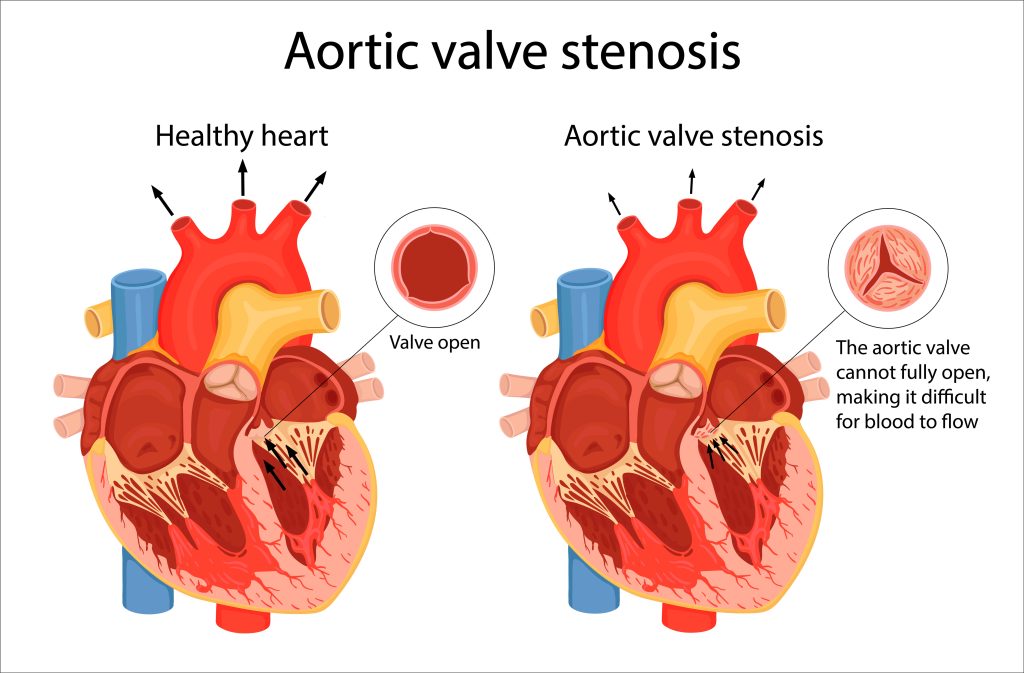
Aortic stenosis (AS) is a medical condition affecting the aortic valve, which regulates blood flow from the heart to the body. It is caused when the aortic valve narrows, leading to restricted blood flow and increased pressure on the heart. This can cause your heart to work harder and strain against the walls of the blood vessels, resulting in fatigue and pain. When this happens, it can interfere with the normal blood flow out of the heart, cause heart damage, and result in a sudden catastrophic event known as a dissection. Dissection can prove to be fatal, leading to death.
Causes of Aortic Stenosis
There are a few causes of Aortic Stenosis. It can be hereditary and may run in families, increasing the risk of the condition. It is also more likely to occur in people aged 40-70 and above due to calcium buildup on the valve over time. Other causes include congenital heart defects, rheumatic fever and radiation therapy. Furthermore, medical conditions such as hypertension, Paget’s disease of the bone, heart failure, kidney disease, and autoimmune diseases can also increase the risk. Last but not least, smoking and untreated infections can also damage the heart valves and increase the risk of aortic stenosis.
Diagnosing Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis is typically detected during a cardiovascular examination, including an EKG and listening for heart murmurs with a stethoscope. Other detection methods include chest X-ray, angiography, cardiac CT scan, cardiac catheterization, and heart MRI.
How Severe is Aortic Stenosis?
Aortic stenosis progresses slowly over several years and can worsen with age and secondary health conditions, such as heart failure, high blood pressure, and diabetes. While aortic stenosis can be a severe condition, its severity depends on various factors, including the extent of valve narrowing and the patient’s age and overall health. The degree of severity can vary from mild to severe. However, as mentioned above, any level of aortic stenosis can lead to significant complications if left untreated.
- Heart Failure: One of the most serious complications of aortic stenosis is heart failure. It happens when the heart is unable to circulate an adequate amount of blood. The heart has to work harder to push blood through the narrow opening as the aortic valve becomes more obstructed. Over time, this can lead to a weakened heart muscle and an inability to pump blood to the rest of the body effectively. Symptoms of heart failure include swelling in the legs and feet, fatigue, shortness of breath, and an irregular heartbeat. Heart failure can sometimes be fatal, particularly if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
- Arrhythmia:Another potential complication of aortic stenosis is arrhythmia or an irregular heartbeat. This can occur because the heart exerts more effort than necessary to circulate blood through the obstructed valve. As a result, it can disrupt the heart’s normal electrical activity. Arrhythmia can lead to symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, and fainting. While it can often be managed with medication or other treatments, it can also be a serious condition that requires close monitoring and intervention.
- Cardiac Arrest: Cardiac arrest is probably one of the most severe complications of aortic stenosis. Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops beating suddenly. In some cases, people with aortic stenosis may experience sudden cardiac arrest without warning signs or symptoms. However, in many cases, cardiac arrest can be preceded by symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fainting. Cardiac arrest is life-threatening if not treated immediately.
Prevention of Aortic Stenosis
AS caused by natural aging is not usually preventable. But one should continue to lead a healthy lifestyle which includes managing diet, exercise, sleep, weight, and being alert to limit the interference of any cardiovascular disease. In addition, there are a few ways you can protect yourself against the development of aortic stenosis. These include:
- Maintain a healthy weight throughout your life by eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly. This helps to keep your blood pressure under control and lowers your risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Maintain healthy heart health by not smoking and following a healthy lifestyle, including getting enough sleep, avoiding alcohol.
- Maintain and protect your blood vessels from damage by staying hydrated, avoiding excessive salt and sugar intake, getting enough exercise, and staying away from excessive sun exposure.
- Aortic stenosis caused by bacterial infection is preventable if infections are treated on time with antibiotics and other medications.
- Aortic stenosis caused by chronic or inherited conditions is not always preventable.
- Periodic monitoring of routine ECG and regular medical checkups.
Summary
AS is most commonly seen in older people, especially after age 65. In some rare instances, children can be born with a defect in the aortic valve that can cause stenosis. Unfortunately, many do not realize they have AS until the condition triggers symptoms such as Pain or tightness in the chest with activity (angina), feeling of dizziness or fainting during activity, tiredness (fatigue), shortness of breath (dyspnoea), irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia) or Heart palpitations, swelling in your legs or they detect it during a medical diagnosis. AS is a complicated problem hence speaking with your doctor at the earliest about AS risks, especially when you have symptoms, can bring in timely intervention. There are advances in surgical and catheter-based techniques that can help treat the cases of older people with multiple conditions that complicate care in their recovery process. Timely or early treatment will ensure a good prognosis. Of course, that needs to be backed by lifelong follow-up and care to lead an everyday life. If left untreated, it can cause severe repercussions. Most do not make it more than a few years without treatment. If treatment is delayed, the extent of Heart damage decides if a full/partial recovery is possible.
FAQs
What is the leading cause of aortic stenosis?
Calcium buildup on the aortic valve that comes with aging and over time is the most common cause of Aortic stenosis, which makes the valve tissue stiff, narrow, and less flexible & hence restricts the blood flow from the Heart to the rest of the body.
How severe is aortic stenosis?
Those with severe Aortic stenosis develop symptoms with a survival rate as low as 50% at two years and 20% at five years without aortic valve replacement.
What are the signs and symptoms of aortic stenosis?
Symptoms of aortic stenosis can include chest pain, troubled breathing, dizziness, heart murmur, rapid or irregular heartbeat, difficulty walking short distances, swelling of ankles and feet, and difficulty sleeping.
What is the life expectancy with severe aortic stenosis?
Aortic stenosis can be dangerous, costly, and debilitating. Chances of survival without treatment for severe symptomatic aortic stenosis are as low as 50% at two years after symptom onset and 20% at five years.
References :
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23046-aortic-valve-stenosis
https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-us/325
https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/aortic-valve-stenosis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557628/
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/150638-overview
https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/aortic-valve-stenosis
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000178.htm
https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-valve-problems-and-disease/heart-valve-problems-and-causes/problem-aortic-valve-stenosis