The Peripheral Vascular System is part of the body’s circulatory system which supplies to & receives blood from all parts of the body except Heart and Brain. The Peripheral Vascular system consists Peripheral Arteries which are responsible for oxygenated blood to get supplied from heart to all body parts, and Peripheral Veins carry deoxygenated blood from the extremities back to the heart.
What is peripheral vascular disease?
Peripheral Vascular Disease or PVD is a blood circulation disorder.
In this condition, your blood vessels narrow or get blocked or spasmed outside the heart and brain.
Peripheral vascular disease can happen in both arteries and veins throughout the body, but often affects the leg’s arteries the most causing fatigue particularly during exercise. This is called intermittent claudication.
One of the major causes of it is arteriosclerosis which is Plaque building up in a vessel and limiting blood flow and oxygen. As plaque build up progresses, it can reduce or completely block the blood flow in that artery leading to organ damage, loss of fingers, toes, etc.
This condition is different from Coronary Artery Disease and Cerebrovascular disease; these are when the narrowing happens in the heart or the brain respectively.
The Types of PVD
There are two types of Peripheral vascular disease: Functional and Organic
Functional PVD
Vessels widen and narrow in response to brain signals, temperatures changes, etc causing a decrease in the blood flow when vessels are narrowing.
There is no physical damage to your blood vessels’ structure in functional PVD
The common causes of Functional PVD are emotional distress, colder temperatures, operating vibrating machinery or tools, drugs.
Organic PVD
This is caused due to Physical damage like plaque Built up, inflammation and more. There is damage to the physical blood vessels’ structure. The primary causes of Organic PVD are diabetes, high cholesterol levels, smoking and high blood pressure.
Risk factors
Some lifestyle factors majorly affect your body, hence putting you at a higher risk for PVD. For instance,
- Overweight,
- Age above 50,
- History of stroke or cerebrovascular disease,
- Abnormal cholesterol levels,
- Family history of
- High cholesterol
- Heart disease,
- Blood pressure
- PVD
- Kidney disease on hemodialysis.
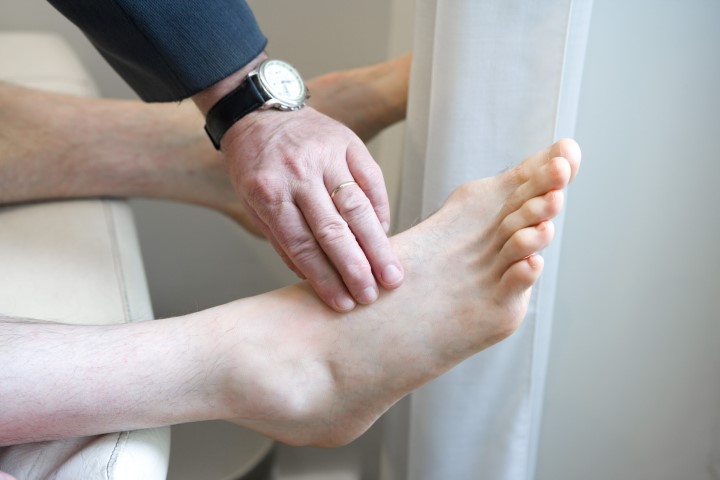
Symptoms of Peripheral vascular disease
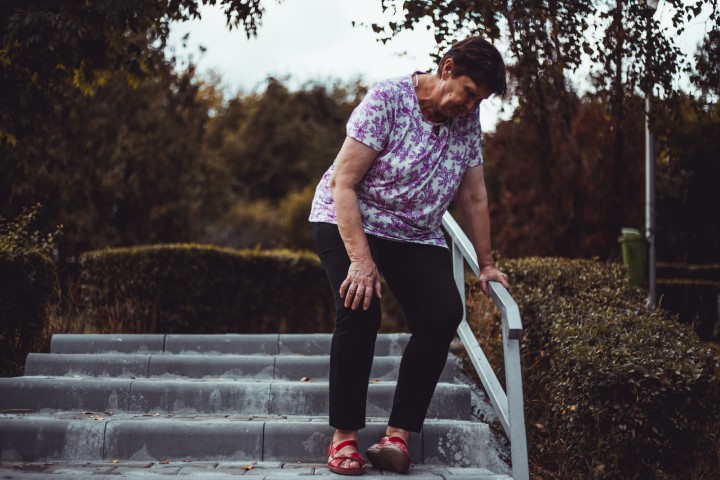



For majority, the first sign of PVD is fatigue and discomfort in your legs and feet, which gradually gets worse due to physical activity and lack of blood flow. This sign is rather slow and irregular but persistent.
The major symptom is Claudication. Claudication is lower limb muscle pain experienced while walking. You may notice the pain increasing when you walk long distances or faster and the pain subsides after some rest, but when the pain returns it takes some time to recede.
Other than the pain, some other symptoms also include
- Reduced hair growth in the legs,
- Cramps while lying in bed,
- Arms or legs turning reddish-blue or even page,
- Legs feeling thin,
- Paler skin,
- Weak pulses,
- Wounds or ulcers that don’t heal,
- Thick opaque toenails, and
- Numbness and heaviness in the muscles.
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, do visit a doctor for a further look. More often than not these symptoms are disregarded as a sign of old age, but delayed diagnosis can lead to complications.
In extreme cases of blood loss, dead tissue can occur. If you suddenly develop a pale, cold limb with weak to no pulse, this is a medical emergency and you require treatment as soon as possible. Untreated limbs as such can lead to amputation.
Treatments for PVD
The treatments for PVD are directed to lower your risk of serious complications and manage your pain and symptoms helping you remain active.
Major lifestyle modifications – Initially treatment.
- Regular balanced diet,
- Exercise daily
- Losing some weight.
- Discontinuing Smoking as it directly causes the reduced blood flow in the vessels, and increases your risk of heart attack or stroke.
Medication
Prescribed by your doctor in order to treat the symptoms.
For instance, medications could be suggested to
- Increase blood flow and relieve symptoms of leg pain
- Reduced blood clotting,
- Lowering high levels of cholesterol and for diabetes may be prescribed
Angioplasty or Vascular surgery
Intervention recommended in cases major artery blockages are diagnosed.
- Angioplasty is when your doctor inserts a catheter into the artery and a balloon is inflated and open into the artery. In some other cases, a stent is used to keep the artery open.
- Vascular surgery, on the other hand, allows the blood to pass the narrow arteries through vein grafting.
If PVD is diagnosed in time, many cases will respond to lifestyle treatments. The best way to examine whether improvement has taken place is to see how far you can walk without pain.
Conclusion
It is imperative to contact your doctor for a clear diagnosis if your legs look pale or blue to you if your legs become cold or you experience chest pain along with leg pain if you find new sores or ulcers have developed but they don’t heal, fever or any other sign of infections.

Comments are closed.