There are different types of Hernia. All of them have common symptoms like a bulge, pain, and pressure. It is important to know what type of pain and at which part of the body so that you can administer the right treatment. Hernias are best treated with surgery.
What is a hernia?
A hernia is an abnormal bulging of abdominal organs when an internal organ pushes through a weak spot in muscle/tissue in the abdominal wall. Typically, you will discover most hernias within the abdominal cavity between the chest and the hips.
Types of Hernia
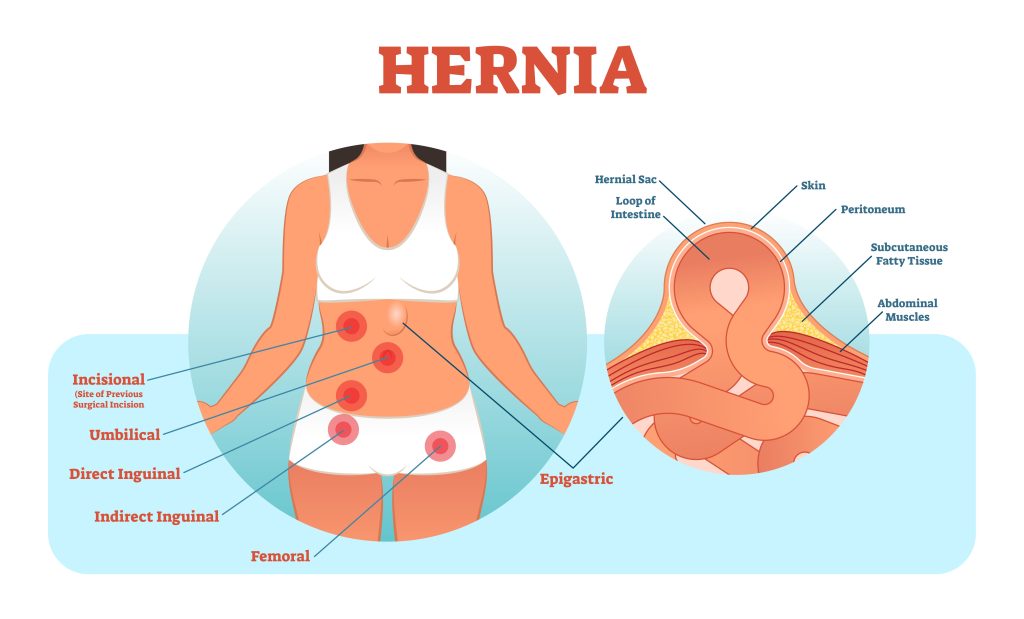
Hernias are divided into several types based on where the bulge is located. A hernia can be congenital, which is present at birth. Or it can be acquired, caused by trauma or other factors. An acquired hernia is a “wound hernia” when abdominal organs protrude through an unnatural opening in the abdominal wall.
The most common types are
a. Inguinal Hernia (Inner Groin) – Mostly occurs in men due to a natural weakness in the groin, where the bladder or the intestine protrudes through the abdominal wall or into the inguinal canal in the groin.
b. Femoral Hernia (Outer Groin) – Most common among women, especially obese or pregnant, where the intestine enters the canal carrying the femoral artery into the upper thigh.
c. Incisional Hernia (as a result of an incision) – Most common among elderly and overweight folks who are inactive after an abdominal surgery, where the intestine pushes through the abdominal wall at the site of abdominal surgery.
d. Hiatal Hernia (Upper Stomach) – Where the upper stomach pushes through the hiatus, an opening in the diaphragm through which the oesophagus passes.
e. Umbilical Hernia (Belly Button) – Most common among newborns and obese women or those who have had many childbirths, where a part of the small intestine passes through the abdominal wall near the navel (aka belly button).
The less common types are
a. Giant Abdominal Wall Hernia – Most typical among those with incisional Hernia or another kind that keeps coming back, is hard to treat and may need surgery to fix it.
b. Epigastric Hernia (Epigastric Region – above the belly button and below the rib cage) – Common among men than women and in some newborn babies, where fat tissues push through a gap between the two sides of the abdominal muscles, namely the belly button and the lower part of the breastbone.
c. Spigelian Hernia – Commonly affects the intestines and omentum, where a layer of fat tissues pushes through the muscle below your navel like split like opening in the fascia.
Causes of Hernia
Increased pressure causes all types of hernias in the abdomen, fascia, and a combination of the following reasons.
a. Bad diet – Poor nutrition and a diet high in sugar can lead to weak abdominal muscles.
b. Bad posture and Balance while lifting heavy objects/weights – Careless lifting of heavy weights and objects without stabilizing the abdominal muscles can lead to a hernia.
c. Disc problems – When the disc in your spine is compressed, it can pressure the nerves that control your muscles. This can cause your abdominal muscles to weaken.
d. Diarrhea, constipation, persistent sneezing, or coughing – These occurrences can weaken the muscles and lead to a hernia.
e. Pregnancy complications – While it’s rare, pregnancy-related weakening of abdominal muscles may lead to a hernia.
f. Poor lifestyle habits – Obesity and smoking can weaken muscles, leading to hernias.
Risk Factors of Hernia
The risk factors for Hernia are,
a. Obesity – If you have a high body mass index (BMI), you are at an increased risk of developing a hernia.
b. Sports injuries – If you’ve experienced frequent sports injuries to your abdomen, you are at an increased risk of developing a hernia.
c. Previous surgery – If you’ve had a previous surgery involving abdominal incisions and the abdominal wall is weak, you are at an increased risk of developing a hernia.
Symptoms of Hernia
The symptoms are many,
– A noticeable swelling, bulge, or lump in the abdomen/groin
– Mild to increased pain, pressure, or swelling at the bulge site.
– Nausea, heartburn, indigestion, constipation, difficulty in swallowing, chest pain, or frequent regurgitation
– Dull aching sensation and feel that something is lodged in your intestines.
– Pain while lifting, laughing, crying, sneezing, or coughing.
Foods and Activities that cause Hernia and relieve Hernia
Exercising too intensely can strain your abdominal muscles and lead to an underlying weakness. This increases your risk of developing a hernia. Binge drinking alcohol can lead to abdominal muscle weakening, which puts you at risk of a hernia.
Drinking warm fluids, such as water, herbal tea, or sugary drinks, can relax the abdominal muscles and relieve hernia pain. Stay hydrated to prevent dehydration and maintain normal urine pressure. Pushing hard during pregnancy or after giving birth can help work out the pressure in your abdominal muscles, relieving the pain of a hernia.
Prevention and Detection of Hernia
Hernias cannot be prevented since they occur due to an accidental combination of medical history and genetic makeup. However, in the interest of good health, we can do the following,
– Make sure you visit your doctor regularly for regular check-ups so they can detect any hernias early.
– Your doctor will likely check your abdomen to feel for a bulge.
– You should inspect your belly button to look for any abnormal bulges.
– Exercising regularly can help you maintain healthy, strong abdominal muscles and prevent them from weakening.
– Avoid any pressure on the abdominal wall like lifting weights
– Refrain from poor lifestyle habits like smoking, drinking, or straining during bowel movements.
– Eat a high-fibre diet and stay hydrated.
Treatment of Hernia
The best treatment for hernias is to prevent them from happening. You should avoid activities that strain your abdominal muscles if you have a hernia. This will help to avoid a hernia. For most hernias, doctors will wait and watch for the abdominal wall to repair and heal but most hernias do not get healed on their own. More significant types of hernias like intestinal hernias may require surgical correction to improve the Hernia and the abdominal wall or prevent an emergency in case of an incarcerated hernia or a strangulated hernia.
Hernia surgery is minimally invasive in most cases for faster recovery and better outcome. In case of umbilical hernia in children, hernia surgery may be recommended if the hernia is large or has not healed by the age of 4-5 years. In case of adults, there are two kinds of surgery available for hernia which the doctor will take a call on the final recommendation –
- Open Surgery – where a cut is made at the site of the hernia, and the protruding tissue is reset and the weakened muscle walls are sutured. A type of mesh is implanted for extra support.
- Laparoscopic surgery – unlike an open surgery but with the same set of repairs, here tiny incisions are made for surgical tools to complete the procedure
Recovery from Hernia
You may be able to resume normal activities after hernia repair. One may need to rest and strengthen their abdominal muscles to prevent a recurrence. In some cases, it is likely to experience pain and discomfort for a few days and may experience constipation or nausea.
The following needs to be kept in mind,
a. It would help if you avoid heavy lifting or straining your abdominal muscles.
b. You should also avoid coughing or straining to pass urine because these can further weaken your weak muscles.
c. You should also drink lots of water to prevent dehydration and maintain normal urine pressure.
d. Follow-up care is essential after hernia surgery. You should return to your doctor for check-ups to ensure no complications.
e. You should also wear a compression garment after surgery to help to reduce swelling and pressure on your incision.
FAQs
1. What is the most common type of Hernia?
Answer – The most common types of Hernia are
– Inguinal Hernia (Inner Groin)
– Femoral Hernia (Outer Groin)
– Incisional Hernia (as a result of an incision)
– Hiatal Hernia (Upper Stomach)
– Umbilical Hernia (Belly Button)
2. What is the most common type of Hernia in males?
Answer – The most common type of Hernia in males is Inguinal Hernia ( Inner Groin) which mainly occurs due to a natural weakness in the groin, where the bladder or the intestine protrudes through the abdominal wall or into the inguinal canal in the groin.
3. What is the most common type of Hernia in females?
Answer – The most common type of Hernia in females is Femoral Hernia (Outer Groin), especially in obese or pregnant women, where the intestine enters the canal carrying the femoral artery into the upper thigh.
4. Are there rare hernias?
Answer – Yes, Spigelian Hernia is a rare hernia.
5. Is Hernia life-threatening?
Answer – An incarcerated hernia can become strangulated and life-threatening if not treated on time.
6. What are the signs of Hernia?
Answer – Hernia signs are pain and a bulge around the abdomen or affected site.
7. What happens if the Hernia is not treated?
Answer – If the Hernia is not treated, it can become life-threatening.
8. Does Hernia require major surgery?
Answer – Yes, an intestinal Hernia may require surgery.
9. How painful is hernia surgery?
Answer – Hernia surgery is not painful because, at the time of surgery, the patient would be administered general anaesthesia. It is the period before surgery and post-surgery during recovery that the patient might experience pain.
10. What is the best treatment for Hernia?
Answer – Timely diagnosis of symptoms, proper lifestyle habits, and medical surgery, where applicable, is the best treatment for Hernia.
11. What foods cause Hernia?
Answer: Fatty, fried food, citrus fruits, spicy food, garlic, onion, and chocolate can trigger hernia symptoms.
12. What foods to avoid in case of Hernia?
Answer – Hernia patients should avoid foods with high sodium, fats and spices, chocolate, garlic and onion, citrus fruits, and fried food in case of Hernia.




Comments are closed.