A coronary artery disease or CAD occurs when there is a build-up in the arteries. In such conditions, it can interrupt the flow of blood to your heart. Plaque causes narrowing or blockage which can result in a greater risk of having a heart attack. Symptoms could include chest pain, discomfort in breathing and shortness of breath.
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally, according to World Health Organisation, it takes an estimate of 17.9 million lives each year. More than four out of five deaths are due to heart attacks or stroke. The most important behavioral risk factors are unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco use and harmful use of alcohol. If you have CAD your doctor might suggest using a stent to treat it. It’s a procedure called Coronary Angioplasty in which the doctor will insert a stent into your coronary arteries. A stent is a small tube made up of metal mesh that is designed to support your artery walls and prevent plaque from blocking your blood flow. It helps the blood flow more freely to your heart. During angioplasty, a thin tube known as a guiding catheter is inserted through the groin or wrist and is then moved towards the site of the blockage. A small balloon at the tip of the balloon catheter is inserted through the guiding catheter near the blocked or narrowed area of the coronary artery. When the balloon mounted with the stent, is inflated, the fatty plaque or blockage is compressed against the artery walls and the diameter of the blood vessel is widened (dilated) to increase blood flow to the heart. Once the plaque is compressed and the artery is opened sufficiently, the balloon catheter is deflated and removed. The stent will remain as a permanent implant in the coronary artery.
Your doctor may use a bare-metal stent(BMS), Drug-eluting stent (DES), or BioResorbable Scaffold (BRS). A drug-eluting stent is the most common type of stent used lately. The new and improved versions of drug-eluting stents are considered safe and effective in most cases. They have ultra-low strut thickness that promotes early vascular healing, the variable strut width, and variable crown design ensure adequate radial strength. However, BRS is a next-generation bioresorbable technology with a low strut thickness of 100 microns which fully resorbs naturally in the artery within 2-3 years, thus restoring the vessel to its true form and nature.
In this blog, you will learn more about Drug-Eluting stents and their benefits.
So what is a Drug-eluting stent?
DES is a standard metallic coronary stent that has a polymer coating and an antiproliferative drug. It allows drug elution into the coronary wall for weeks and months after stent implantation. It releases medication directly into your artery which helps the scar tissues from forming within the stent and narrowing your blood vessels again. That’s how Drug Eluting stents work you might need to take additional medications including blood thinners after the procedure.
Benefits of Drug-Eluting Stent
They can prevent plaque build-up, relieve chest pain, and promote good blood flow to your heart. They may also lower your chances of having a heart attack.
As it’s a less invasive procedure than coronary bypass surgery, which is recommended to people who have more than two narrowed arteries. So most people recover within few days of inserting the stent. A stent helps you get back to your regular schedule faster. In contrast, coronary bypass surgery takes six weeks or more to recover.
With Benefits, Drug-Eluting Stents even have risks:
Like any medical procedure, coronary angioplasty or stenting do involve risks, including:
- Bleeding or clotting
- Damage to your blood vessel
- Infection
- Kidney damage caused by the dye
- Allergic reaction to the anesthetic, dyes, or other material used
- Scarring of your blood vessels
- Heart attack and stroke, which is rare
If you form scar tissue after stenting, the doctor may need to repeat the procedure. In case you have chest pain report to your doctor immediately as it could be a sign of serious complication.
There are also few other things you should consider before getting a drug-eluting stent.
For patients with a history of bleeding problems, a drug-eluting stent might not be a good option. Apart from this, you might need to take blood thinners for the rest of your life to prevent your blood from thickening and causing the risk of clots in the stent. Your doctor would give you additional information on what to expect before and after angioplasty.
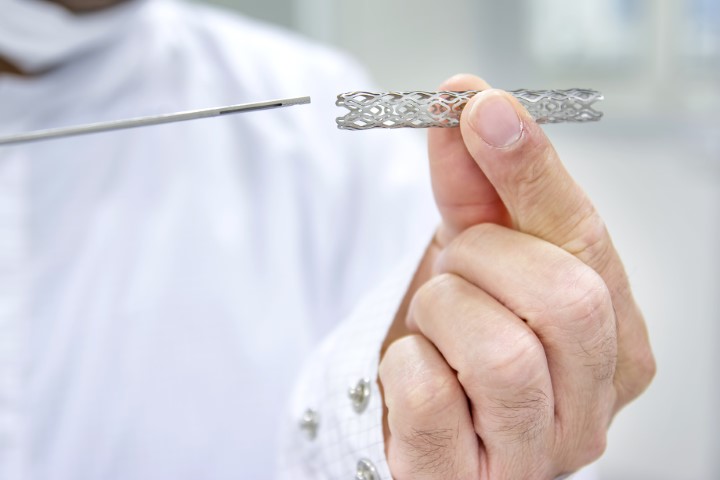



How to live with a stent?
Having a stent doesn’t mean you have to live differently. But you will have to take extra care of your heart by eating right and healthy. Be active and take your medications. Follow few precautions such as:
- Take your blood-thinning medication this would prevent heart attack and stroke. After stenting, you will take aspirin plus another antiplatelet for at least 6 months. If you are at a high risk of bleeding your doctor with shortening the duration of these medicines. Work with your doctor to decide how long you will be needing the medications. The decision depends upon your risk of having a heart attack, risk of bleeding, and your preferences about taking the medicines.
- Stent identification card- Your doctor will provide you with a stent identification card that you can show to your health professionals so that they know you have a stent.
Protect your heart health
You can lower your risk of developing blocked arteries or having a heart attack by practicing healthy habits. Common risks for heart disease include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and being overweight. All of which can be managed with a healthy lifestyle. For example, having a balanced diet and regular exercising can go a long way towards keeping your heart healthy and strong. Smoking would put you at risk. If you are a smoker then now would be a good time to call quits.
If you are diagnosed with CAD, to prevent complications follow your doctor’s instructions and treat it. Drug-eluting stents are a good option for patients with CAD but they are only one part of the solution. You may have to take statins, aspirin, or other medications.
Follow your doctor’s advice and take their prescribed medicines and also follow their recommended lifestyle which will keep your heart healthy.



Comments are closed.