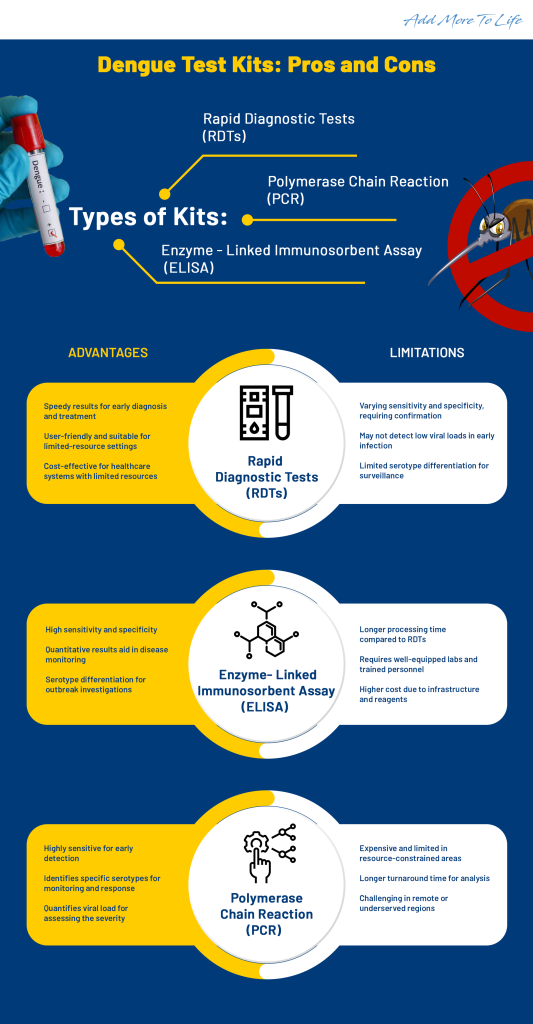
Types of Dengue Test Kits
Several types of Dengue test kits are available to diagnose the disease. These include rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, i.e. (ELISA), and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests. Each test has its advantages and limitations, which we will discuss in detail.
1. Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs)
RDTs are simple, easy-to-use tests that provide rapid results within 15 to 20 minutes. They work by detecting the presence of dengue-specific antibodies or antigens in a patient’s blood. RDTs are designed to be performed at the point of care, such as in clinics or field settings, without requiring specialized laboratory equipment.
Advantages of RDTs:
- Speed: RDTs provide quick results, enabling early diagnosis and prompt initiation of appropriate treatment.
- Ease of use: RDTs are user-friendly and can be performed by healthcare providers with minimal training.
- Portability: RDT kits are portable and do not require sophisticated laboratory infrastructure, making them suitable for resource-limited settings.
- Cost-effective: RDTs are relatively inexpensive compared to other diagnostic methods, making them affordable for healthcare systems with limited resources.
Limitations of RDTs:
- Sensitivity and specificity: This can vary depending on the manufacturer and the stage of the disease. False-positive or false-negative results can occur, requiring confirmation with other tests.
- Timing: RDTs may not detect the dengue virus during the early stages of infection since the viral load is low. Therefore, repeat testing may be necessary if dengue is suspected despite a negative RDT result.
- Limited serotype differentiation: RDTs may not differentiate between dengue virus serotypes, essential for epidemiological surveillance and outbreak investigations.
2. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Tests
ELISA tests are laboratory-based tests that detect dengue-specific antibodies in a patient’s blood. They involve multiple steps and require specialized laboratory equipment. ELISA tests can differentiate between IgM and IgG antibodies, which helps determine the infection stage.
Advantages of ELISA Tests:
- Sensitivity and specificity: ELISA tests have high sensitivity and specificity, especially when performed appropriately after symptom onset.
- Quantification: ELISA tests can provide quantitative results, allowing the measurement of antibody titers, which can help monitor disease progression or response to treatment.
- Serotype differentiation: Some ELISA tests can differentiate between dengue virus serotypes, which is valuable for surveillance and outbreak investigations.
Limitations of ELISA Tests:
- Turnaround time: ELISA tests require more time for processing compared to RDTs. Results may not be available for several days, depending on the laboratory capacity.
- Laboratory infrastructure: ELISA tests necessitate well-equipped laboratories with trained personnel, which may not be available in all healthcare settings, especially in resource-limited areas.
- Cost: ELISA tests are more expensive than RDTs due to the need for laboratory infrastructure and specialized reagents.
3. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Tests
PCR tests are highly-sensitive molecular diagnostic tests that detect the dengue virus’s genetic material (RNA) in a patient’s blood. PCR tests can accurately determine the presence of the virus and differentiate between different dengue virus serotypes. However, PCR tests are complex and require sophisticated laboratory equipment and trained personnel.
Advantages of PCR Tests:
- Sensitivity and specificity: PCR tests are highly-sensitive and specific, providing accurate results even during the early stages of infection, especially when the viral load is low.
- Quantification: PCR tests can identify the specific dengue virus serotype, which is crucial for surveillance, monitoring, and outbreak response.
- Serotype differentiation: PCR tests can quantify the viral load, which helps assess the infection’s severity and monitor the response to treatment.
Limitations of ELISA Tests:
- Cost and infrastructure: PCR tests are expensive and require well-equipped laboratories with trained personnel, limiting their availability in resource-constrained settings.
- Turnaround time: PCR tests typically take several hours, including sample processing and analysis. Rapid results may not be achievable, especially in remote or underserved areas.


Conclusion
In conclusion, a timely and accurate diagnosis of dengue fever is essential for effectively managing and controlling the disease. Different types of dengue test kits, including rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) tests, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, are available for diagnostic purposes.
Choosing the appropriate test depends on the specific requirements of the healthcare setting, the availability of resources, and the stage of the infection. Different test types may be necessary for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of dengue fever.
It is crucial to continue investing in the development of diagnostic technologies that are more accessible, affordable, and rapid without compromising accuracy, to combat dengue fever effectively. This will enable early detection, prompt treatment, and efficient surveillance, ultimately contributing to preventing and controlling dengue outbreaks worldwide.
FAQs
Q: What is the advantage of using rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) for dengue fever diagnosis?
A: RDTs offer quick results, usually within 15 to 20 minutes, allowing for early diagnosis and timely initiation of appropriate treatment. They are easy to use, portable, and cost-effective, making them ideal for point-of-care testing in resource-limited settings.
Q: Are rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) as accurate as other dengue test kits?
A: While RDTs provide rapid results, their sensitivity and specificity can vary depending on the manufacturer and the stage of the disease. False-positive or false-negative results are possible, and confirmation with other tests may be required.
Q: How do enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) tests differ from rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs)?
A: ELISA tests are laboratory-based and can differentiate between IgM and IgG antibodies, providing information about the stage of the infection. They have higher sensitivity and specificity than RDTs but require longer turnaround times and well-equipped laboratories.
Q: What is the advantage of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests for dengue fever diagnosis?
A: PCR tests are highly-sensitive and specific, capable of detecting the genetic material of the dengue virus. They can identify the specific serotype of the virus and quantify the viral load, aiding in disease monitoring and assessing the severity of the infection.
Q: Are polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests widely available and affordable?
A: PCR tests are complex and require advanced laboratory infrastructure and trained personnel, making them more expensive and less accessible in resource-constrained settings. They also take several hours to complete, which can delay results compared to rapid tests like RDTs.




Comments are closed.