While planning parenthood, caring for a woman’s reproductive and sexual health should be paramount for every couple. Family planning means timing one’s pregnancy and the subsequent, with proper spacing between pregnancies. It could be to prevent pregnancy or treat infertility in women.
Prevention of pregnancy in women could be achieved through various contraceptive methods that may include implants, intrauterine devices (IUDs), use of oral contraceptive pills, sponges, injectables, condoms, patches, vaginal rings, male and female fertilization, and fertility awareness to name. These methods are long-acting reversible, short-acting reversible, or permanent methods.
This blog discusses one such contraceptive method, the IUD insertion procedure, and how women planning an IUD insertion should prepare themselves and what they can expect from the procedure to arrive at an informed decision and remove any apprehension.
How to Prepare for IUD Insertion?
Though a simple and safe contraceptive method with a short procedural time, women undergoing IUD insertion may experience anxiety and stress with a host of questions about the pros and cons of the procedure, which is normal. It is better to talk with the healthcare provider to address this concern and ensure a healthy state of mind while preparing for the treatment. One needs to know the following to make an informed decision about the procedure.
What is an IUD?
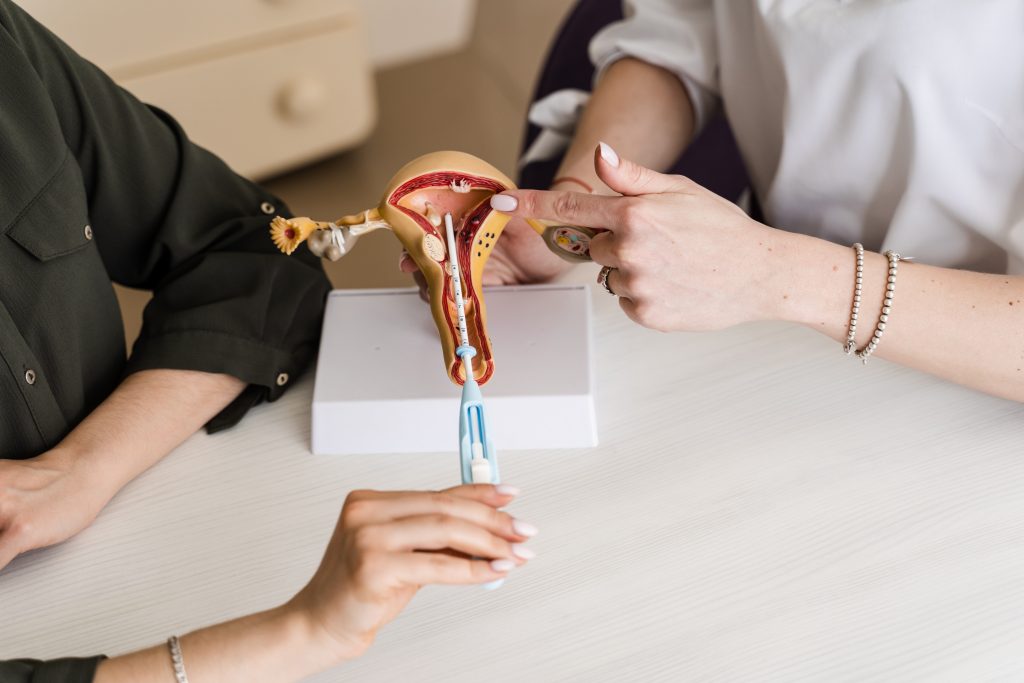
An intrauterine device is a small T-shaped birth control device an obstetrician, gynecologist, or healthcare professional inserts in the woman’s uterus to prevent her pregnancy. It is one of the long-acting reversible contraceptive methods (LARC). An IUD can be removed anytime a woman wants to conceive or stop using it. An IUD has a string at the bottom that extends to the vagina, enabling the health provider to remove the device when required.
What are the different types of IUDs?
The IUDs come in two types- A copper IUD and a hormonal IUD.
- Copper IUDs – Copper IUDs release copper ions into the uterus. This copper acts as a spermicide. The IUDs are solely used for contraceptives and contain no hormones.
- Hormonal IUDs- Hormonal IUDs release progestin-like hormone, levonorgestrel (LNG), a synthetic form of progesterone hormone that prevents ovulation. With no egg, sperm cannot contribute to fertilization. In cases of chance, the body ovulates, and this hormone thickens the cervical mucus, thus preventing the sperm from reaching the egg for fertilization. These IUDs also help in controlling menstrual bleeding or cramps.
The difference between the progestin-like hormone LNG and progesterone is that LNG is an artificial hormone similar to progesterone. Progesterone is a steroid hormone secreted by a woman’s reproductive system.
How does IUD insertion work?
IUD insertion is a simple procedure to insert an IUD in a woman’s uterus who is planning contraception. The professional healthcare provider uses a small speculum, an instrument to widen the vagina walls to examine and insert an IUD. The procedure takes a few minutes and may cause a little pain to the woman undergoing it while the procedure is taking place. Patients may experience varied levels of pain.
Know if you are the right candidate for the treatment
Pregnant women or women with a history of vaginal or cervical cancer, vaginal infection, or sexually transmitted infection (STI) cannot have IUD insertion. Those with cardiovascular health issues must inform their doctor before planning an IUD. The healthcare provider may, if required, ask for a pregnancy or STI test to know if one is eligible for IUD insertion.
How to address anxiety?
Working with a healthcare professional for help and guidance to ease and relieve stress through proper education and consultation will make the procedure less painful and more successful.
What to Expect from IUD Insertion?
Understanding what to expect from the treatment before going to the doctor or the clinic is advisable to have a stress-free and relaxed mindset to avoid unresolved questions and related anxiety. In the case of IUD insertion, one may expect the following-
A simple procedure
IUD insertion is a simple procedure that takes a few minutes. IUDs can be inserted only by a healthcare professional.
Several benefits
IUDs have the following benefits: –
- IUDs are safe and effective contraceptive methods with a high success rate.
- They are cost-effective and reversible options. One may get them removed when deciding to become pregnant.
- They are easy to use without interfering with the routine activities.
- They are less bothersome than contraceptive oral pills since once inserted, one does not have to worry about adhering to any regular timetable of having contraceptives.
Some side effects
Some of the expected side effects of IUDs may include-
- Headaches, mood swings, nausea, breast tenderness, in the case of hormonal IUDs.
- Initial changes in menstrual bleeding that may go away after some time.
- Painful periods and an increase in bleeding with copper IUDs.
- With hormonal IUDs, ovarian cyst growth is also expected in some cases when women ovulate or release an egg every month that does not fertilize.
- Irregular periods and frequent spotting are expected in cases with hormonal IUD insertion, during the first few months.
Prevent pregnancy but do not protect against STIs
IUDs only protect against pregnancy; hence, one must use condoms to protect oneself from STIs.
Safe and effective
Copper IUDs are effective immediately upon their insertion. The effectiveness of hormonal IUDs depends on where one is in their menstrual cycle. Till the hormonal IUDs provide protection, one must use alternative control methods.
Conclusion
Intrauterine devices are safe and effective measures to prevent pregnancy, ensuring a healthy reproductive and sexual life for women. As a long-acting reversible contraceptive, they provide a long-term birth control solution until removed. For a successful and satisfying medical outcome of the procedure, every patient must stay informed and be aware of the treatment, the types of IUD options, how the device works, the associated risks and benefits, the pre and post-procedural care, the preventive measures if any, and any issue of concern relating to the procedure and/or the device.
References
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325097#Preparation
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/24441-intrauterine-device-iud
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/long-acting-reversible-contraception-iud-and-implant
https://www.webmd.com/sex/birth-control/iud-intrauterine-device#:~:text=for%20their%20recommendation.-,How%20Soon%20Do%20IUDs%20Start%20Working%3F,7%20days%20to%20be%20effective.