While the thought of cancer as a whole is daunting, one needs to understand that the disease presents itself in different forms. In essence, cancer is when the cells within a body start to mutate at an unnatural pace & cannot be stopped. While this is the common form, many women suffer from a variation of it called Ovarian Cancer.
Ovarian cancer occurs when cancerous growths begin at the ovaries. The female reproductive system has two ovaries on either side of the uterus. The ovaries are responsible for producing eggs (ova) as well as releasing the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Ovarian cancer usually goes undetected in the early stages. In most cases, it is detected only when cancer has spread to the pelvis and the abdomen, making it difficult to treat. If the tumors are benign (non-cancerous) in nature, they are confined to the ovaries and do not spread. However, if the tumors are malignant, they spread to the nearby organs and can be fatal.
What are the types of ovarian cancer?


The ovaries are made up of three types of cells. Each of them can develop into a different kind of ovarian cancer. The different types of ovarian cancer are:
Epithelial Tumors: These tumors begin from the cells that cover the outer surface of the ovaries. Over 90% of ovarian cancers are epithelial tumors. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous), borderline (low malignant potential), or malignant (cancerous).
Ovarian Stromal Tumors: These tumors start from the structural tissue cell that produces the female hormones – estrogen and progesterone. These tumors can be diagnosed at an earlier stage as compared to the other types of ovarian tumors.
Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors: Germ cells are responsible for producing eggs (ova) in women. These tumors begin in the germ cells. Most germ cell tumors are usually benign. This rare type of ovarian cancer tends to occur in younger women.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
In the early stage, ovarian cancer hardly causes any symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose. Advanced-stage ovarian cancer may cause certain symptoms that may often be mistaken for other common, benign conditions or illnesses.
Some of the most common symptoms of ovarian cancer include bloating/swelling in the abdomen, feeling full quickly while eating, change in bowel habits, pain/discomfort in the pelvic area, frequent urination, and loss of weight.
In case these symptoms are more frequent and don’t go away soon, it is advisable to visit your doctor and rule out the possibilities of ovarian cancer. If you have a family history of ovarian cancer, you may talk to a medical practitioner about the risk of developing the same.
How is ovarian cancer diagnosed?
After analyzing your symptoms, if the doctor suspects ovarian cancer, he/she will conduct a pelvic exam to diagnose the condition. During the pelvic exam, the doctor will insert gloved fingers into the vagina, while simultaneously pressing the abdomen to examine your pelvic organs. The doctor also examines your external genitalia and cervix visually.
The doctor may also suggest imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan to determine the size and the shape of the ovaries. Imaging tests can also show if a mass of tissue is present in the pelvic area, but they cannot confirm if the mass is cancerous. Blood tests may also be conducted to determine the presence of tumor markers that indicate ovarian cancer.
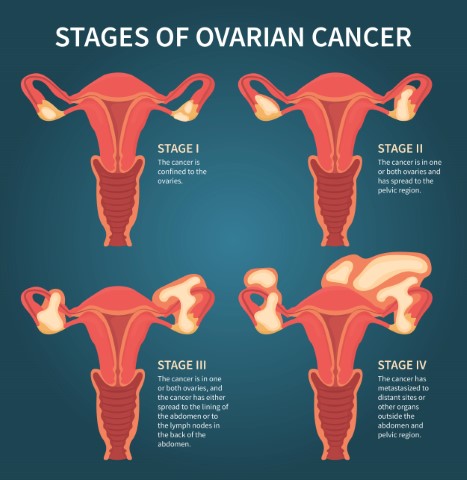
After diagnosing ovarian cancer, the next step would be to stage cancer to finalize the treatment options.
What does ovarian cancer surgery involve?
Surgery is not only one of the main treatment methods for ovarian cancer, but it is also a diagnostic tool to determine ovarian cancer. The goal of the surgery for ovarian cancer is to know how far cancer has spread and removed as much of the tumor as possible. The type of surgery will depend on the stage of cancer and your overall health.
Before the surgery, your doctor may run blood and urine tests a week before to ensure that you are healthy enough to undergo the surgery. Your doctor may also take a chest x-ray and ECG to check your heart rhythm.
Surgery for ovarian epithelial tumors:
The surgery for ovarian epithelial cancer has 2 main goals – staging and debulking.
Staging: This is the first goal of ovarian cancer surgery. Staging is done to see how far cancer has spread from the ovary to the organs. This process involves removing the uterus, along with both the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Some samples of the lymph nodes in the pelvis and abdomen are taken through biopsy. Staging is extremely important as it helps determine the best way to treat the condition.
Debulking: The next goal of the surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This is known as debulking. This is especially important if cancer has spread across the abdomen. Debulking is done to ensure that no tumor larger than 1 cm is left behind.
Surgery for ovarian stromal tumors:
In most cases, ovarian stromal tumors are confined to just one ovary. So, the affected ovary will be removed through the surgical procedure. If cancer has spread further, the tissues in the surrounding areas may have been removed. The main goal of the surgery for ovarian stromal tumors is to remove cancer.
Surgery for ovarian germ cell tumors:
For most ovarian germ cell tumors, the uterus, both ovaries, and the fallopian tubes are removed. If the cancer is confined to just one ovary and you want to retain the ability to bear children, only the affected ovary and the fallopian tube are removed.
Depending on the type and stage of ovarian cancer, your doctor may choose the type of surgery along with other treatment methods such as chemotherapy. Though the surgery will ensure that the cancerous tumors have been removed, it is important to follow up with your healthcare practitioner on the after-care and the possible side effects of the surgery. You can also incorporate certain lifestyle changes to keep yourself healthy and prevent a relapse.



Comments are closed.