What Is Aortic Stenosis?
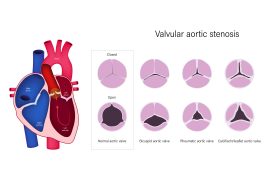
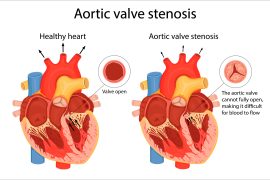
Aortic stenosis is a condition in which the aortic valve in the heart becomes narrowed or blocked, making it difficult for blood to flow properly from the heart to the rest of the body. Therefore, the heart has to work harder to pump blood, leading to strain and potentially causing severe heart problems. These include heart failure and even sudden cardiac arrest.
Symptoms of Aortic Stenosis
The symptoms of aortic stenosis can vary, and they may not always be noticeable. In the early stages, people may not experience any symptoms at all. However, as the condition progresses, the symptoms become more noticeable and can lead to significant health problems. Let us take a look at the symptoms of aortic stenosis.
Chest pain:
One of the most common symptoms of aortic stenosis is chest pain. The pain may be described as pressure or tightness in the lungs or the chest. It can occur during physical activity or even while resting.
Shortness of breath:
Shortness of breath can occur during physical activity or even while resting. People with aortic stenosis may feel like they are running out of breath, especially when they are not exerting themselves. As the condition progresses, the heart may struggle to pump enough blood to fulfill the body’s requirements, causing a feeling of breathlessness.
Dizziness and fainting:
Dizziness and fainting are severe symptoms of aortic stenosis. They can occur due to a highly decreased blood flow to the brain, resulting in dizziness and loss of consciousness. Fainting indicates that aortic stenosis is advanced and requires immediate medical attention.
Fatigue:
Fatigue is another common symptom of aortic stenosis. It can be caused by the heart’s inability to pump the required blood to meet the body’s energy needs. As a result, people with aortic stenosis may feel tired or weak even after getting enough sleep.
Heart Palpitations:
Heart palpitation, rapid or irregular heartbeat, can feel like the heart is skipping a beat, fluttering, or racing. In people suffering from aortic stenosis, palpitations can occur due to the heart working harder to compensate for the narrowed valve. This can cause an irregular heartbeat, also known as an arrhythmia, leading to palpitations.
Reduced Hunger And Body Weight:
These are less common symptoms of aortic stenosis but can occur in some patients. These symptoms are typically seen in severe cases of aortic stenosis, where the reduced blood flow can impact the digestive system and cause a loss of appetite. Additionally, the increased workload on the heart can result in the body burning more calories than usual, leading to unintentional weight loss. While reduced hunger and weight loss can indicate aortic stenosis, they are not specific to this condition. Other underlying health issues can also cause them.
Recognizing the symptoms of aortic stenosis is important because early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. In addition, aortic stenosis is a progressive condition, which means it will worsen over time if left untreated. By recognizing the symptoms of aortic stenosis early, patients can receive prompt medical attention and begin treatment to slow down the progression of the disease.
In severe cases, aortic valve replacement surgery may be necessary. Early detection can improve the chances of a successful outcome. Therefore, recognizing the symptoms of aortic stenosis is crucial for ensuring and improving the quality of life for those with this condition.
The severity and progression of symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause of aortic stenosis. Understanding the causes of aortic stenosis can help patients, and their healthcare providers determine the best treatment and management.
Underlying Causes of Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis is commonly caused by age-related wear and tear of the aortic valve or calcium buildup on the aortic valve. However, there are other causes of aortic stenosis, including congenital and acquired forms.
Congenital aortic stenosis is a condition that is present from birth. It occurs when the aortic valve is not formed correctly during foetal development.
Acquired aortic stenosis, on the other hand, is the most common cause of aortic stenosis. It occurs later in life due to other factors, such as calcium deposits on the aortic valve, which can lead to the narrowing and hardening of the valve.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatment Options
If aortic stenosis is suspected, the doctor will perform a physical exam and may order diagnostic tests like an Echocardiogram, Chest X-ray, CT scan, Stress test, or Cardiac MRI to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment options for aortic stenosis depend on the severity of the condition. In some mild cases, medication may be prescribed, and lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, getting regular exercise, and quitting smoking, would be recommended to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
While in other severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the aortic valve. Aortic valve surgery is an effective treatment option for aortic stenosis. Some of the treatment options are:
Balloon valvuloplasty:
Balloon valvuloplasty involves inserting a catheter with a balloon on the tip into the narrowed aortic valve. This balloon is then inflated to widen the valve and improve blood flow.
Surgical aortic valve replacement:
This procedure involves replacing the damaged aortic valve with a mechanical or biological valve. During the surgery, the chest is opened, and the damaged valve is removed and replaced with a new valve.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) Or Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR):
TAVR is minimally invasive, and it involves inserting a catheter with a new valve on the tip through a small incision in the groin or the chest area. The catheter is guided to the damaged aortic valve, and the new valve is then implanted, replacing the damaged valve. TAVI or TAVR is a less invasive option than surgical aortic valve replacement. It may be suitable for patients who are not candidates for surgery.
Conclusion
Aortic stenosis is a severe heart condition that requires prompt medical attention. It can lead to significant health problems if left untreated. Therefore, it is important to recognize the symptoms of aortic stenosis for early detection and treatment. While the symptoms of aortic stenosis can be frightening, the good news is that effective treatment options can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. As a result, people with aortic stenosis can lead healthy, fulfilling lives with the right diagnosis and treatment.
FAQs
Q. What is aortic stenosis?
A. Aortic stenosis is a heart condition that occurs when the aortic valve, which regulates blood flow out of the heart, becomes narrowed or blocked. This can make it difficult for blood to flow properly throughout the body.
Q. What are the symptoms of aortic stenosis?
A. The most common symptoms of aortic stenosis include chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, fatigue, and heart palpitations. These symptoms can indicate that the heart is not functioning correctly, and it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Q. What causes aortic stenosis?
A. Age-related wear and tear on the aortic valve, and calcium buildup on the aortic valve are the common causes of aortic stenosis. However, congenital heart defects and other medical conditions, such as rheumatic fever, can also lead to the development of aortic stenosis.
Q. How is aortic stenosis diagnosed?
A. Aortic stenosis can be diagnosed by your healthcare provider through physical examination or using a variety of diagnostic tests like an Echocardiogram, Chest X-ray, CT scan, Stress test, or Cardiac MRI. These tests allow doctors to evaluate the heart’s function and determine the severity of the condition.
Q: How can aortic stenosis be prevented?
A: While aortic stenosis cannot be prevented entirely, some measures can be adopted to reduce the risk of developing the condition. These include exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and managing high blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Q. What are the treatment options for aortic stenosis?
A. Treatment for aortic stenosis depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, the symptoms may be managed by medication. Surgery becomes necessary in more severe cases requiring repair or replacement of the aortic valve. Aortic valve surgery is an effective treatment option that can improve the quality of life for people with aortic stenosis.



Comments are closed.