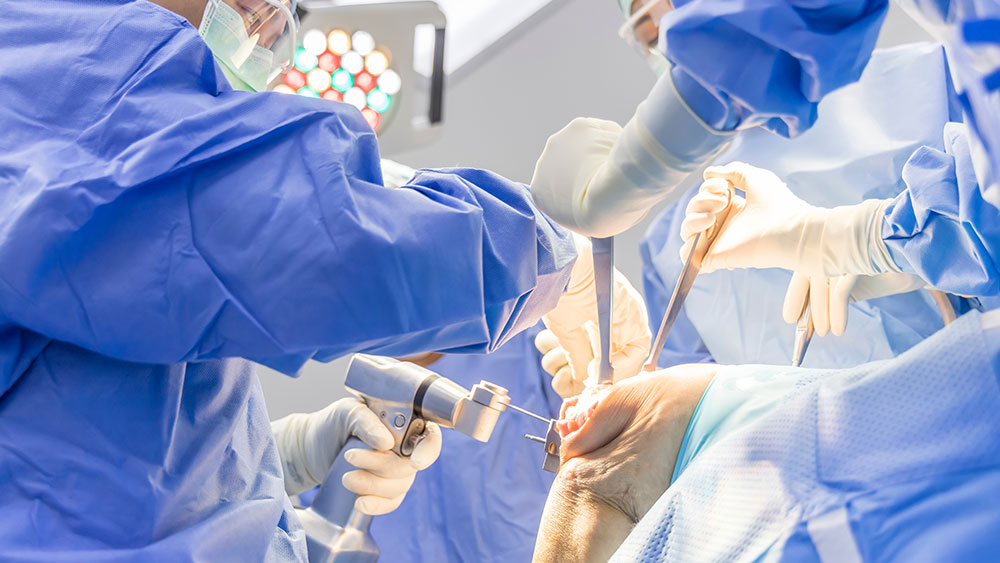
Introduction – What is joint replacement?
Anatomically, a joint is that part of the body where two or more bones meet, and there are different kinds of joints in the human body – like hinge joints and ball-and-socket joints. In the 1880s, a brilliant German doctor named Themistocles Gluck invented the first joint replacement. As we understand it, joint replacement is a surgical procedure where a damaged joint (due to age, accident, or condition) or parts of it are replaced with a prosthesis made of plastic, metal, or metal-based alloys or ceramic. It is designed to replicate the exact movement of a natural healthy joint. The most commonly performed joint replacements are that of the total knee and the hip, as well as partial knee resurfacing, wrist, elbow, shoulder, and ankle. Of course, joint replacement has come a long way, and we have robotic surgery taking the world of orthopaedic treatment to the next level with its precision and outcome.
What is robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery is an advanced form of surgery in which orthopaedic surgeons uses a patient’s computed tomography (CT) scans to build a 3D model of the patient’s bone. With that virtual model as a guide, the surgeon then uses the robotic arm to make accurate bone cuts and insert the components more precisely than conventional methods. It can be used to treat a variety of orthopaedic conditions, including bone deformities or fractures
Difference between robotic and conventional knee replacement surgery
Compared to conventional knee replacement surgery where human intervention is more prevalent, in an advanced robotic surgery, the degree of human intervention is minimal, and chances of human error are almost next to negligible. In such a scenario, robotic surgery enables the surgeon to execute the said procedure with utmost precision whether it is deformity correction or implant selection, and overall virtual simulation in the pre-planning stage to ensure a consistent and desired surgical outcome.
Advantages of using robots in the medical and healthcare field
Robotic surgery reduces the risk of infection and complications compared to conventional surgery. It also results in a shorter length of stay for the patient and quicker rehabilitation. With robotic surgery, the procedure takes less time and less tissue damage happens. Since robotic surgery is generally easier to learn and more efficient than conventional surgery, more procedures will likely be performed with robots in the future.
How and why are robots used in surgery?
Robotics is a technology that allows the surgeon to control a surgical robot that assists during the procedure in real-time. The surgeon can use the robot to perform and assist in various operations. The robot is programmed to perform the surgery exactly as per planning done by the surgeon and with greater precision.
Who is the ideal candidate for robotic knee replacement surgery?
Typically, patients who have knee arthritis consider knee replacement surgery when the quality of life is significantly affected because of pain and functional limitations. Of course, people differ in what they consider “significant” quality of life changes as well as their tolerance for pain. Some people consider knee arthritis a significant problem if it prevents them from participating in sports or taking extended walks. Other people do not consider knee arthritis to be a significant problem until pain interrupts sleep or affects their ability to do even simple activities, such as household chores.
Before recommending a knee replacement surgery, an orthopedic surgeon will conduct a thorough examination of your knee using X-rays and possibly an MRI to see inside of it. They will also go over your recent medical history before deciding whether or not surgery is necessary to go for knee replacement surgery.
Advantages of Robotic Knee Surgery
Advantages of robotic knee replacement
The main advantage of robotic knee replacement is the reduction in error, massive improvement in accuracy, the precision of the procedure, and the outcomes associated with it in the form of a lower infection rate. Robotic knee replacement surgery also has the following advantages.
Reduced recovery time – Patients who have had robotic surgery report a faster recovery than patients who have had traditional knee replacement surgery. Patients return to work or sports sooner than patients who have had traditional knee replacement surgery.
Fewer complications – Researchers attribute the low rate of complications in robotic knee surgery to there being less human intervention leading to less chance of human error and, hence minimizing complications.
Less pain – Patients who have had robotic knee replacement surgery find the operation much less painful than conventional knee replacement surgery. The robotic system can be programmed to deliver the exact amount of cuts on the knee, reducing the amount of pain the patient experiences.
The success of robotic knee replacement surgery
The robotic knee replacement surgery procedures successfully provided quicker rehabilitation and lesser hospital stay. It is personalized and more precise. Moreover, it provides a more predictable and consistent outcome.
Conclusion
As the robotic system helps in better preoperative planning, optimal alignment, and precision in bone cutting hence it is associated with improved early functional recovery and reduced time to hospital discharge compared with conventional total knee arthroplasty. For patients interested in robotic surgery, it is essential to consult a board-certified orthopaedic surgeon to discuss the option thoroughly.
FAQs
-Is robotic surgery safe(r)?
Answer– Yes, experts recommend robotic surgery as safe because there is minimal risk of infection and complications due to less human intervention.
-Is robotic surgery painful?
Answer – Compared to traditional procedures, robotic surgery is less painful because of less tissue damage.
-Is robotic surgery widely performed?
Answer – Yes, robotic surgery is quite widely performed in most major Indian cities and different parts of the world.
-Is robotic surgery better than regular surgery?
Answer – In terms of medical technology advancement and patient ease and comfort, robotic surgery is recommended, but the final call on the kind of surgery a patient undergoes depends on the extent of joint damage and the surgeon’s advice.
-How effective is robotic surgery?
Answer – Robotic surgery is very effective. Most hospitals list this surgery as a day procedure, and it is very effective with its shorter recovery period, accuracy, and precision at the time of surgery and fewer chances of infection and pain.
-What is the best type of knee surgery?
Answer – The best type of knee surgery depends on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s
recommendation of the procedure. In terms of medical technology, robotic knee replacement surgery will always be preferred for the various advantages in terms of precision, accuracy, and outcome.